Our High-Performing Core Network
Fully virtualizable on VMware, K8S, Docker and OpenStack containers
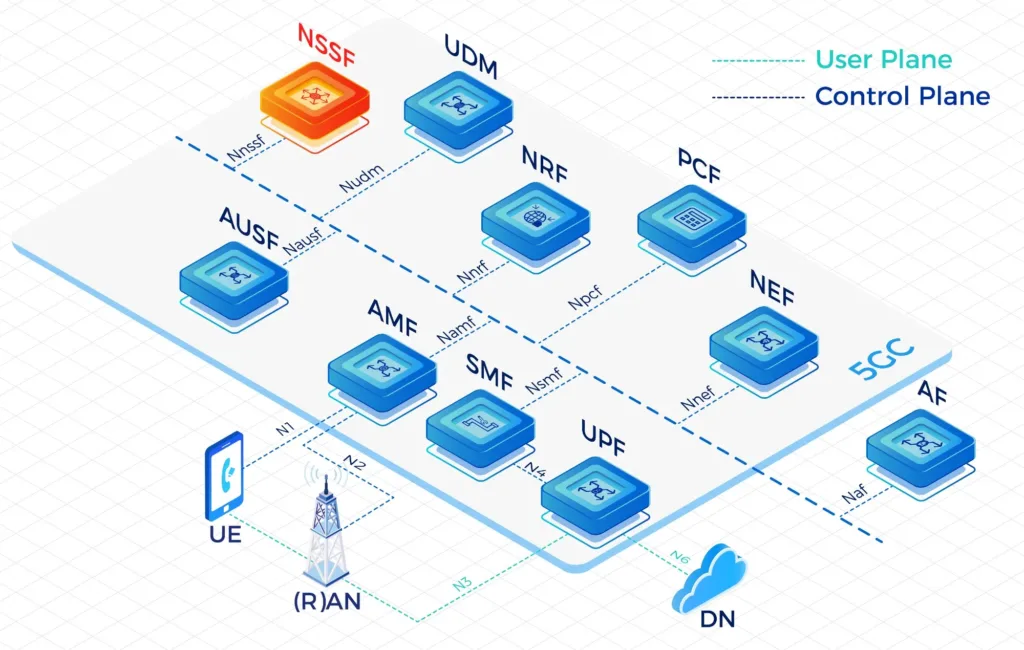
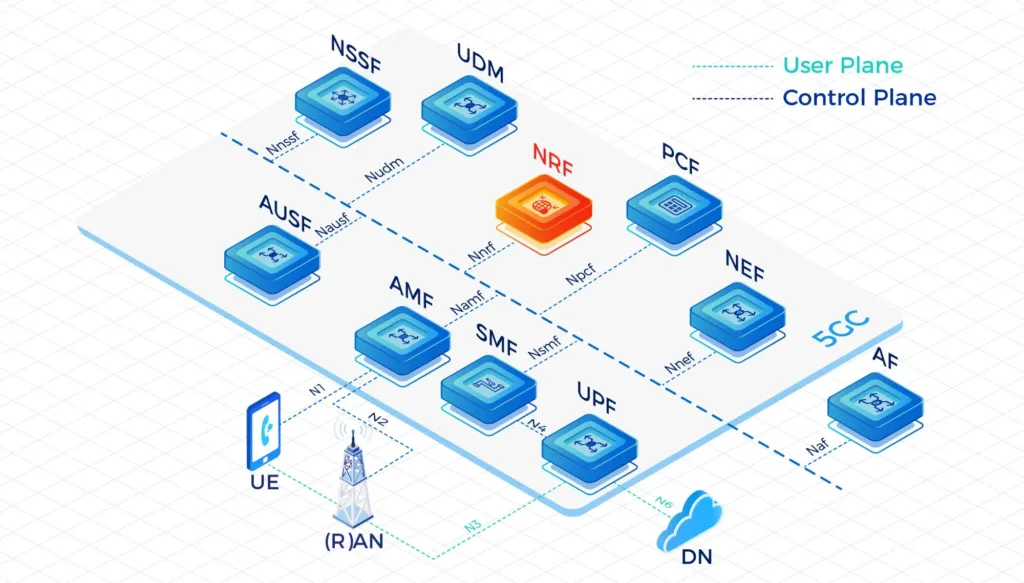
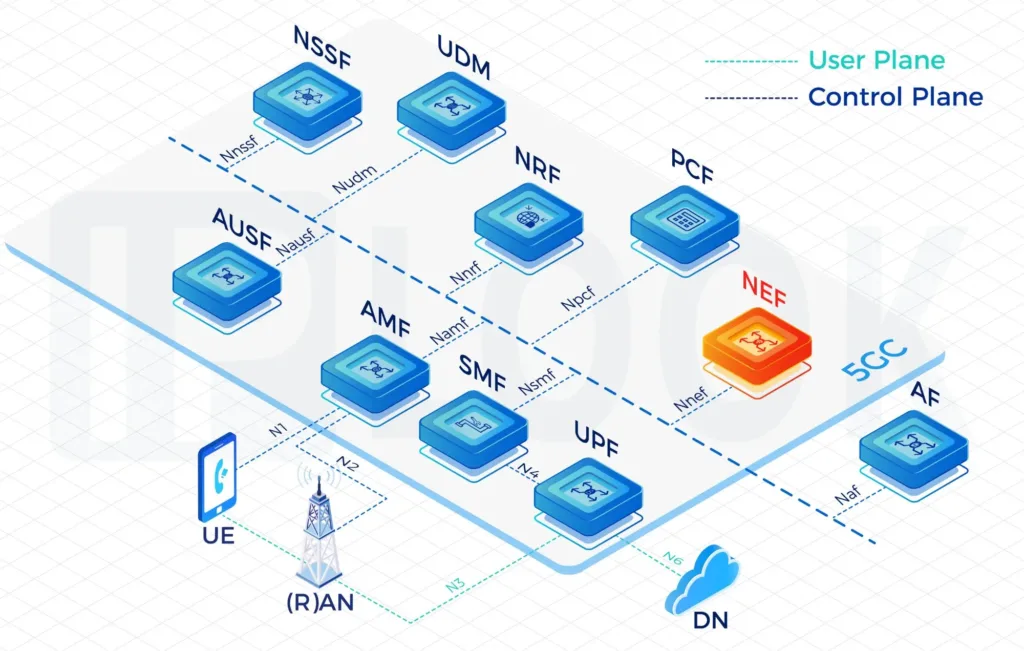
User Plane Function(UPF)
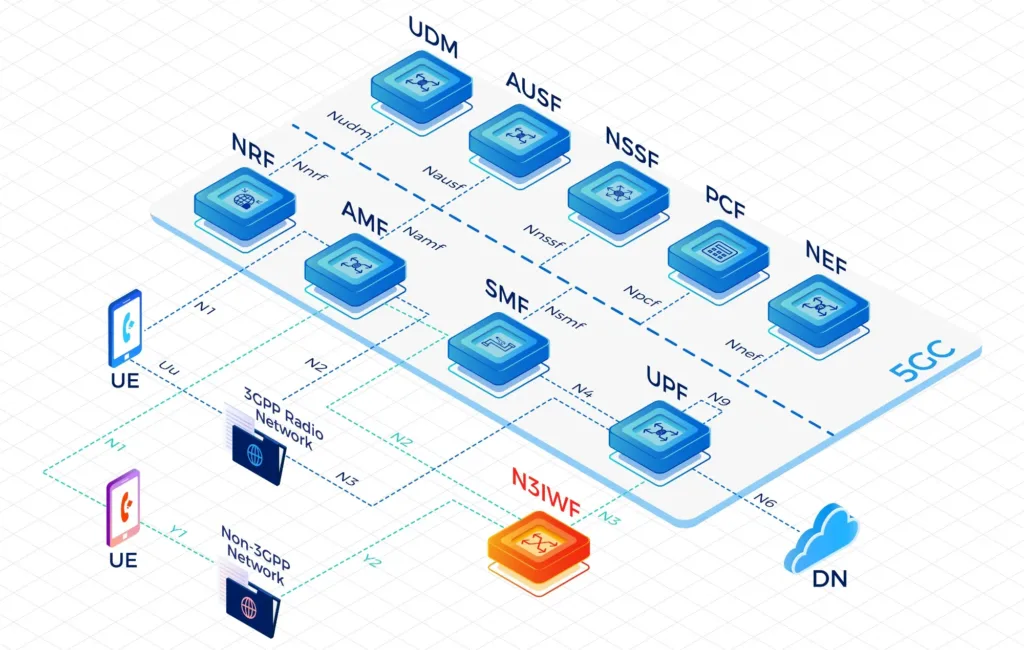
The User Plane Function (UPF) represents the data plane evolution of a Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS) strategy, which is a fundamental component of the 3GPP 5G core network(5GC).
The UPF plays the most critical role in the process of data transfer. It provides the interconnect point between the mobile infrastructure and the Data Network (DN), i.e. encapsulation and decapsulation of GTP-U.
Key Benefits

Fully Virtualized, Highly integrated, Cloud Native UPF
Perfect compatibility with third-party core network elements

5GC UPF Multi-Gbps support: 10GB/25GB/40GB/100GB

Enabled for centralized or distributed data centers

Highly scalable
Enable to deploy on Cloud Platform such as AWS and Azure

High performance, low cost solution
Single instance throughput is up to 100Gbps
IPLOOK's Most Scalable, High Performance UPF
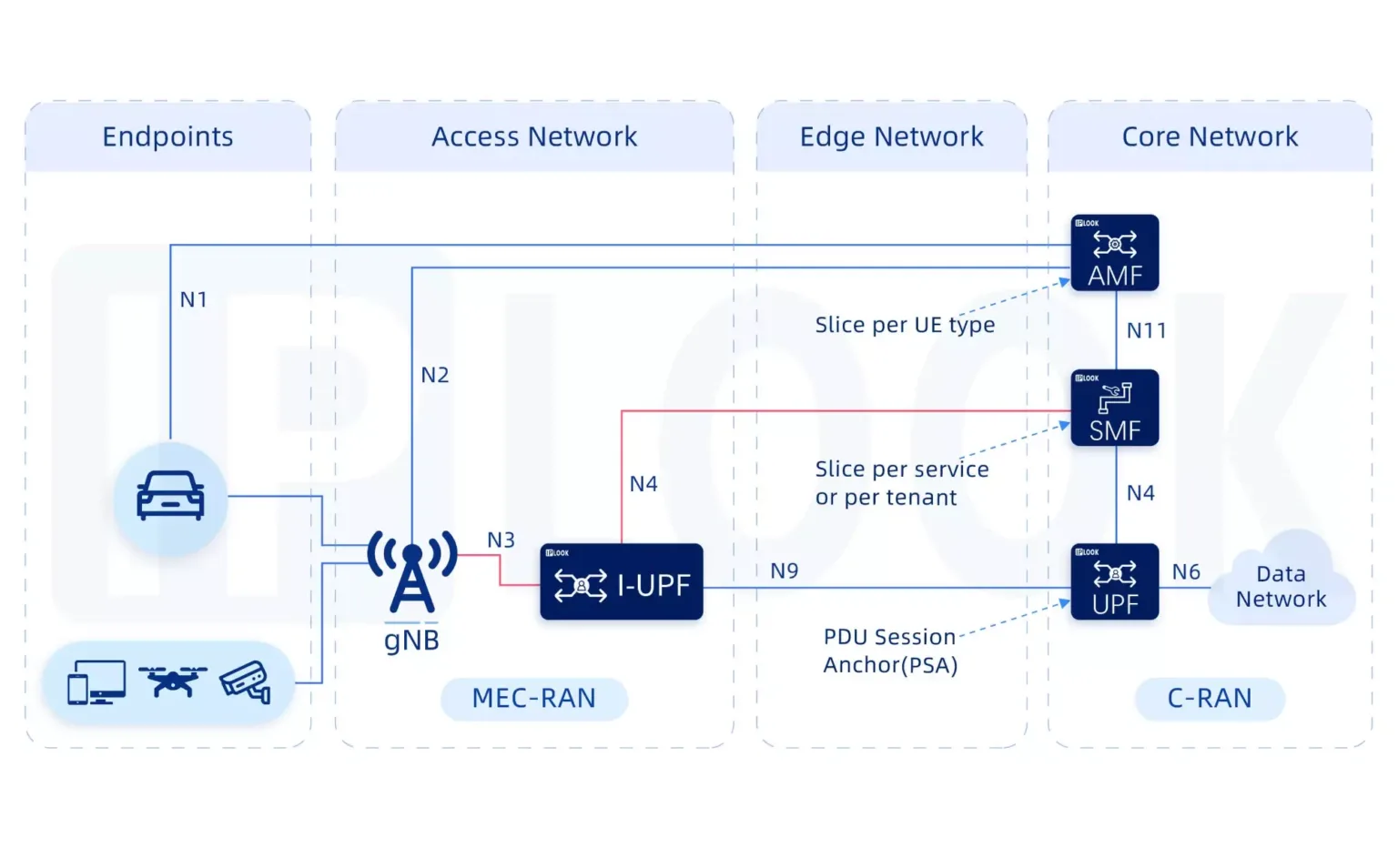
- The IPLOOK UPF has been designed to be distributed and virtualized in 5G and offering better that 4G EPC which was designed to be more centralized in the mobile core network and running on COTS server. UPF can be co-located in the new emerging cloud edge data centers.
- Data transfer process in 5GC though UPF:
Firstly, the data is sent by an terminal equipment, which will be transmitted over a wireless channel to gNodeB. Then, the gNodeB encapsulates the user data into GPRS Tunnelling Protocol for the user plane (GTP-U) packets. Here comes the most important part, the User Plane Function(UPF) receives users’ data from N3 interface and then sends them to the DN. - IPLOOK‘s Standalone UPF within its 5G Core Network(5GC) enables serving both 4G and 5G Radio Access Networks(RANs). Single 5GC UPF instance throughput is up to 100Gbps.
Features
Comply to 3GPP R15/R16 Standards
Four distinct reference points:
- N3: Interface between the RAN (gNB) and the (initial) UPF
- N9: Interface between two UPF’s (i.e the Intermediate I-UPF and the UPF Session Anchor)
- N6: Interface between the Data Network (DN) and the UPF
- N4: Interface between the Session Management Function (SMF) and the UPF
IP Protocol Stack Basic Function
- ARP
Routing Function
- Static Routing
- Direct Routing
- IP Policy-based Routing
- Routing Policy
Distributed Packet Core Basic Function
- Supporting SSC Mode 1
- Supporting SSC Mode 2
Basic Service Function
- Session Management
- Path Management
- Data Forwarding
- Address Assignment
- User Plane Address Assignment
- QoS and Traffic Management
Element Management System(EMS) supported
IPv6 Basic Function
- IPv4/IPv6 Dual Stack Access
- IPv6 Networking on Gi/SGi/N6
Availability Function
- DDoS Attack Proof
Operation and Maintenance
- KPI Management
- Fault Management
- Log Management
- Configuration Management
- License Management
- Security Management
- Tracing Function
- Online Support
- Online Loading
- SSH
- Availability
QoS Management Basic Function
- Supporting Reflective QoS
Basic Charging Function
- Time Based Charging of Service
- Volume Based Charging of Service
Charging Mode
- Offline Charging
Open Northbound interface and graphical web based management interface
- API
- RESTful