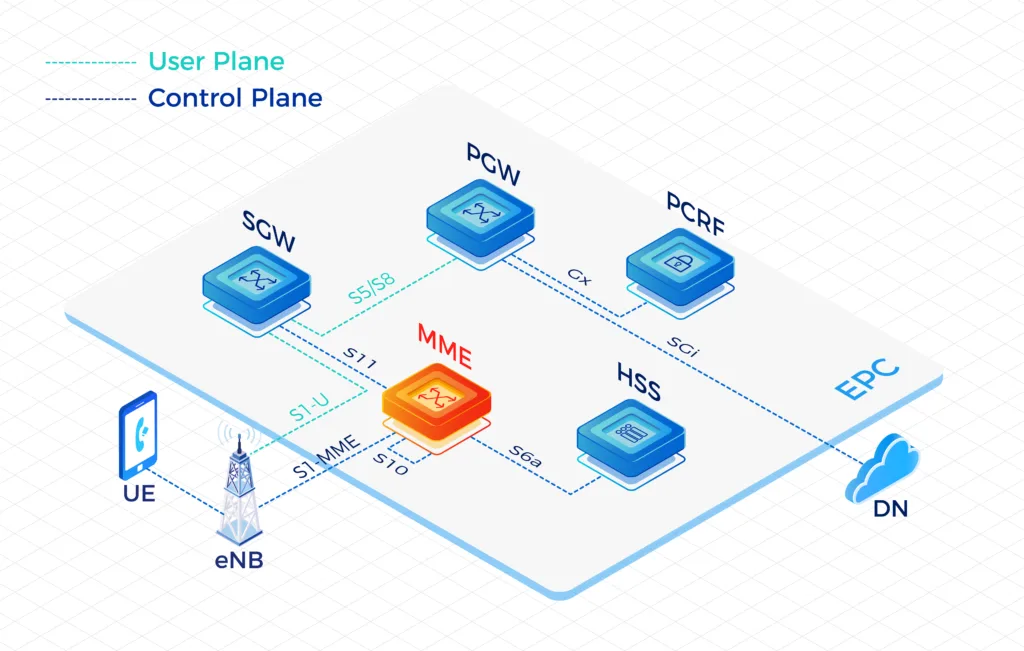
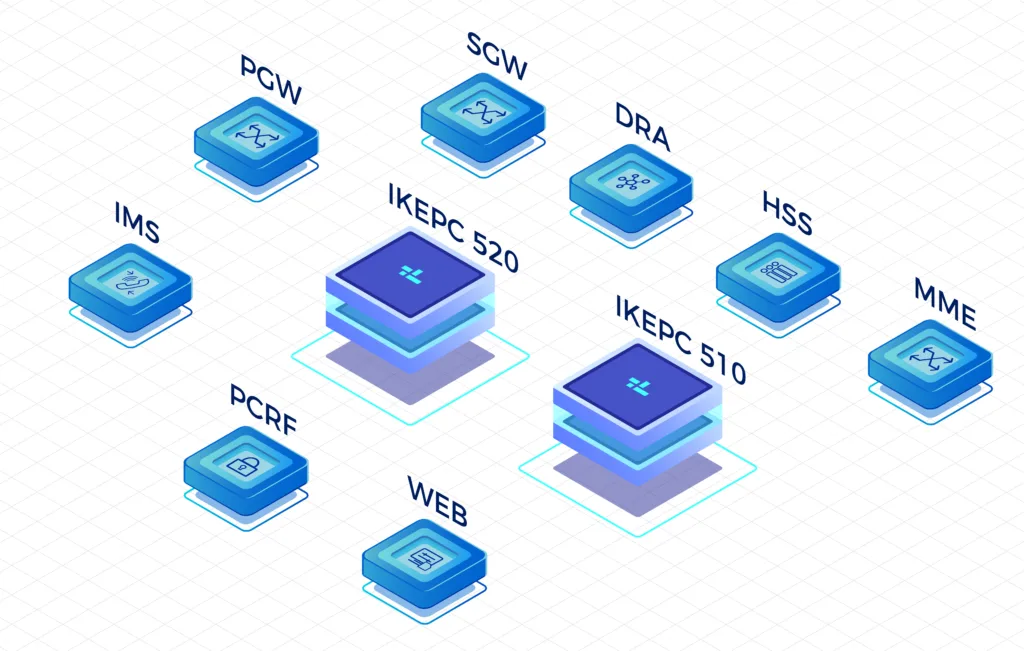
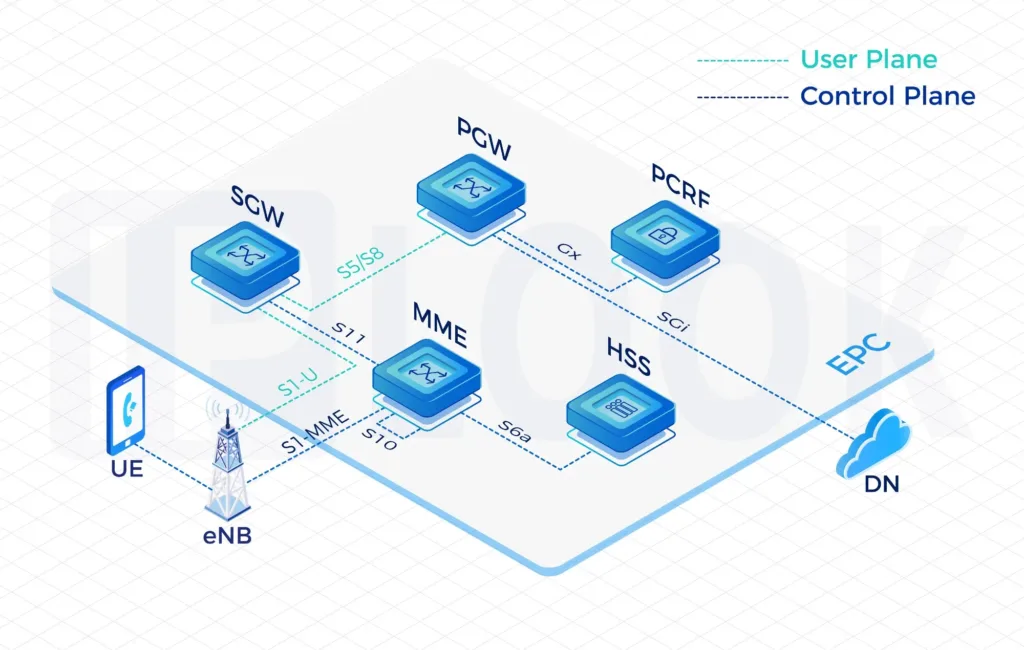
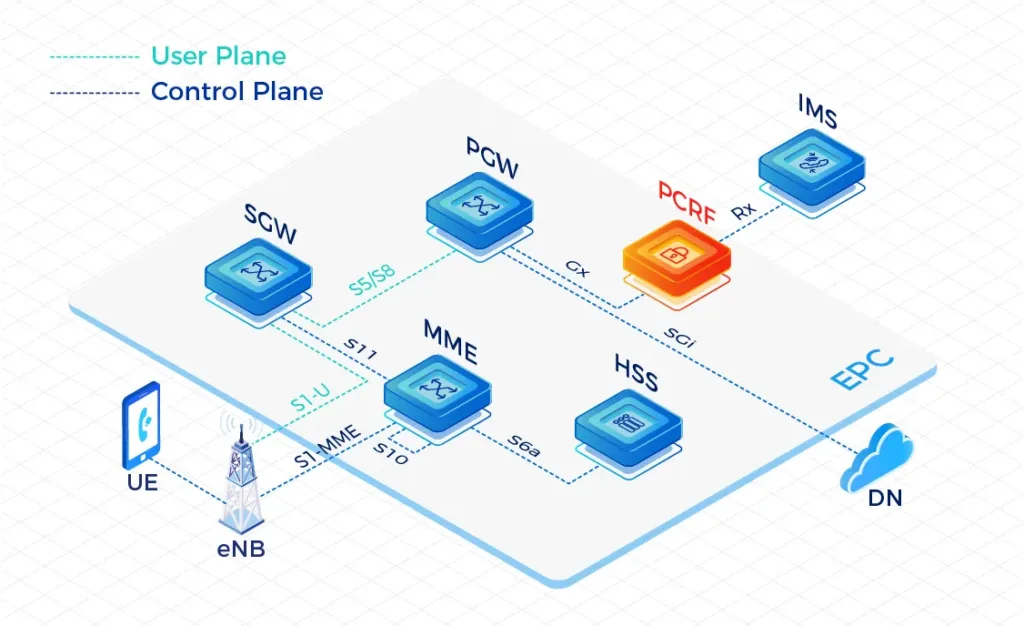
Our High-Performing Core Network
Fully virtualizable on VMware, K8S, Docker and OpenStack containers
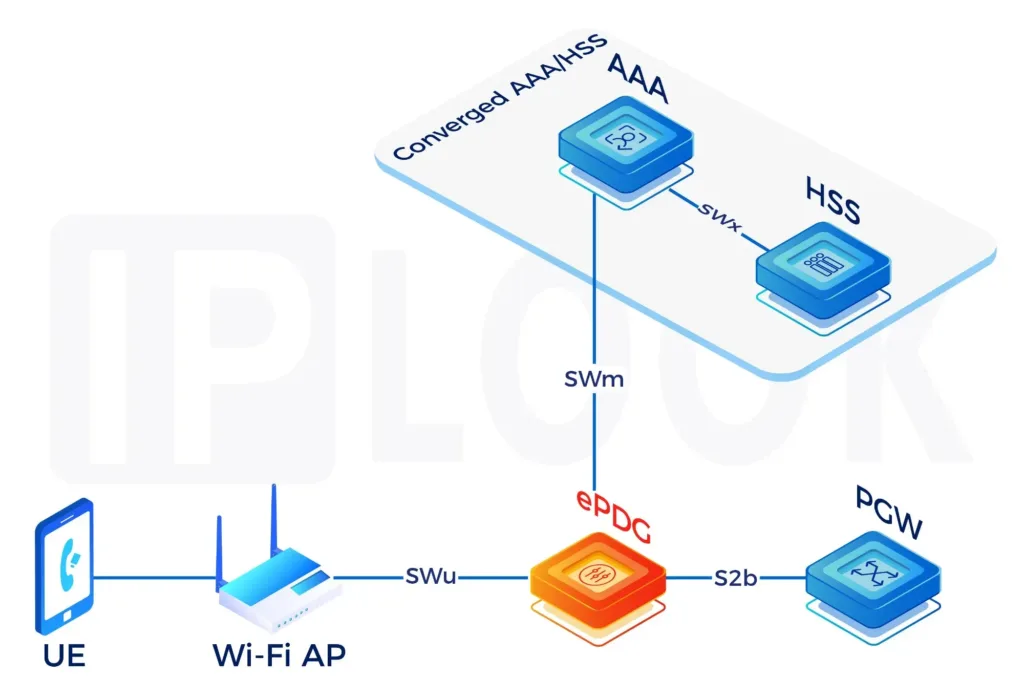
Evolved Packet Data Gateway(ePDG)
The ePDG (Evolved Packet Data Gateway) is a key component in the LTE core network, primarily used to support the security, compatibility, and high-quality service transmission for access to the LTE network via untrusted non-3GPP access (such as Wi-Fi). The ePDG ensures encrypted transmission of user data by establishing IPSec tunnels, providing a solid guarantee for operators to achieve Wi-Fi and LTE network convergence, enhance user experience, and facilitate traffic offload.
Key Benefits

Full Protocol Stack Standard Support
Highly compatible, simplifies integration and speeds deployment
High-Reliability Disaster Recovery Capability
Ensures service continuity, avoids single point of failure risks, meets carrier-grade high availability requirements.

End-to-End Secure Encryption
Ensures the confidentiality and integrity of user data during public network transmission, defends against man-in-the-middle attacks.

Dynamic Seamless Switching Capability
Enhances user experience and ensures continuity of VoWiFi/VoLTE voice services.

Intelligent Local DNS Resolution
Reduces reliance on external DNS, optimizes traffic scheduling efficiency, and lowers network latency.

Emergency Service Priority Assurance
Meets public safety regulations and expands emergency service coverage scenarios.
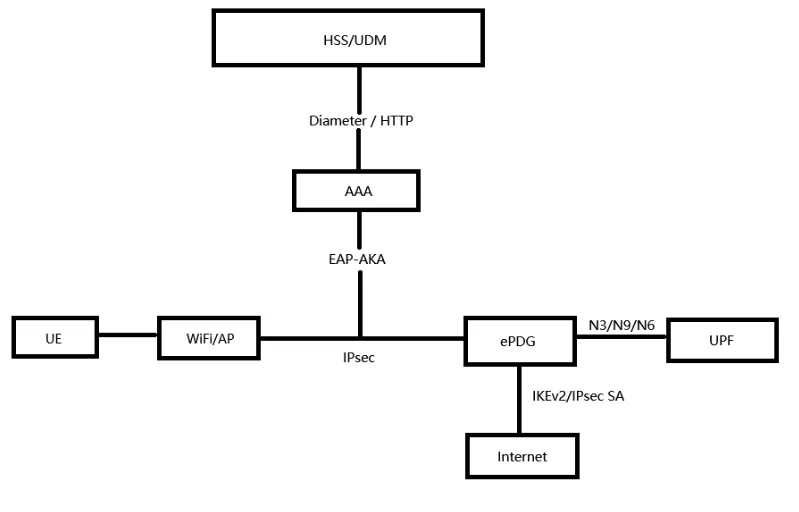
ePDG Secure Access Technology
- ePDG (Evolved Packet Data Gateway) is a key network element in the 5GC core network responsible for non-3GPP access (such as Wi-Fi). It establishes IPsec secure tunnels with user devices via the public network to enable encrypted communication and authentication, ensuring secure user access.
- ePDG supports collaboration with AAA/HSS to complete EAP-AKA based authentication processes, and forwards user data to the core network (e.g., UPF, IMS, or Internet) via S2b or N3/N6 interfaces.
- Distributed ePDG deployment can be extended to the edge network to achieve local traffic offloading, reduce latency, and alleviate transmission pressure. This meets the low-latency, high-security requirements of 5G services and is a key enabler for multi-access convergence and VoWiFi applications.
Features
Interface Functional Features
- SWu
- Handles exchange conflicts per RFC 7296
- Supports dynamic key update for IKE SA and Child SA
- DPD detects inactive terminals and clears contexts automatically
- SWu
- Supports SCTP multi-path and HSS active-standby switching
- S2b
- Built-in DNS, dynamically selects PGW address by APN/PLMN
Protocol Functional Features
- Diameter
- Transport over SCTP or TCP
- Supports connection setup, capability negotiation (CER/CEA), heartbeat (DWR/DWA), and status management
- IKEv2
- Key update and lifecycle management for IKE SA / Child SA
- Supports SA negotiation (IKE_SA_INIT), authentication (IKE_AUTH), notifications (INFORMATIONAL), NAT traversal, and identity protection
- ESP
- Tunnel mode encryption of IP packets with DES/3DES/AES and MD5/SHA1 integrity
- GTP
- GTP-U: User plane transmission via TEID tunnels
- GTP-C: Session and mobility management (Create/Modify/Delete)
Process Functional Features
- Detach: Releases session and IPSec tunnel resources
- Registration: Establishes IPSec tunnel via IKEv2, completes authentication and session setup
- Handover: Seamless switching between 3GPP and non-3GPP access (e.g., WiFi-LTE handover)
- Emergency Services: Supports emergency calls without SIM cards, bypasses regular authentication
Advanced Features
- QoS Assurance: High-priority scheduling for emergency services
- Dynamic Load Balancing: Distributes PGW traffic based on local DNS weight
- Disaster Recovery Backup: Supports active-standby HSS switching and SCTP multi-path redundancy
Security Features
- Integrity Check: Prevents data tampering (MD5/SHA1)
- Data Encryption: Encrypts user data via ESP tunnel mode
- Identity Protection: Encrypts identity information exchange using IKEv2