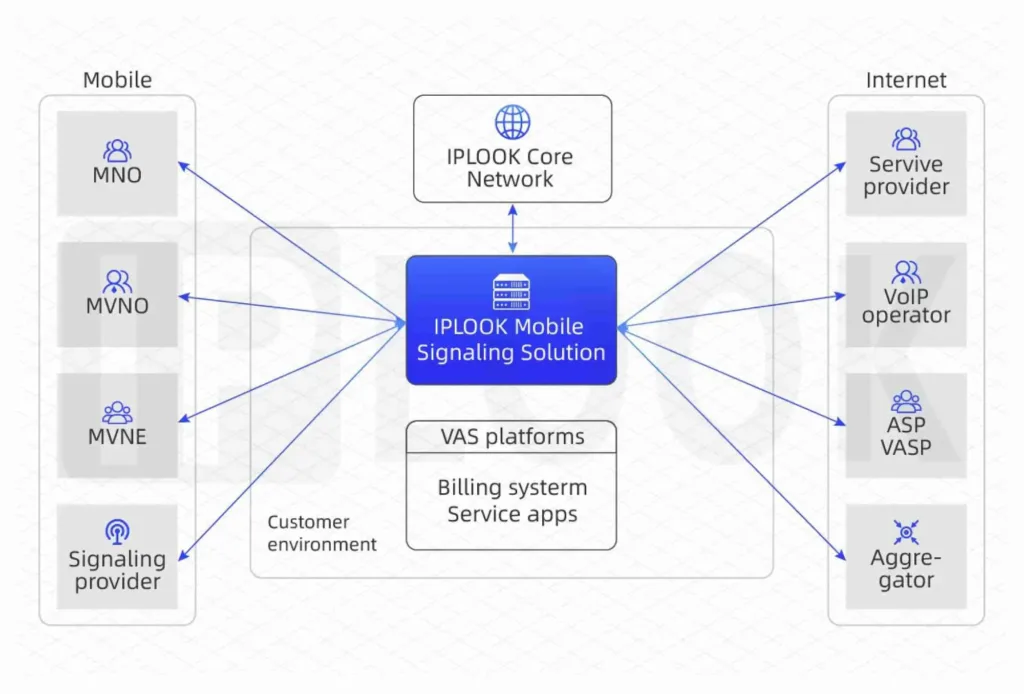
Our High-Performing Core Network
Fully virtualizable on VMware, K8S, Docker and OpenStack containers
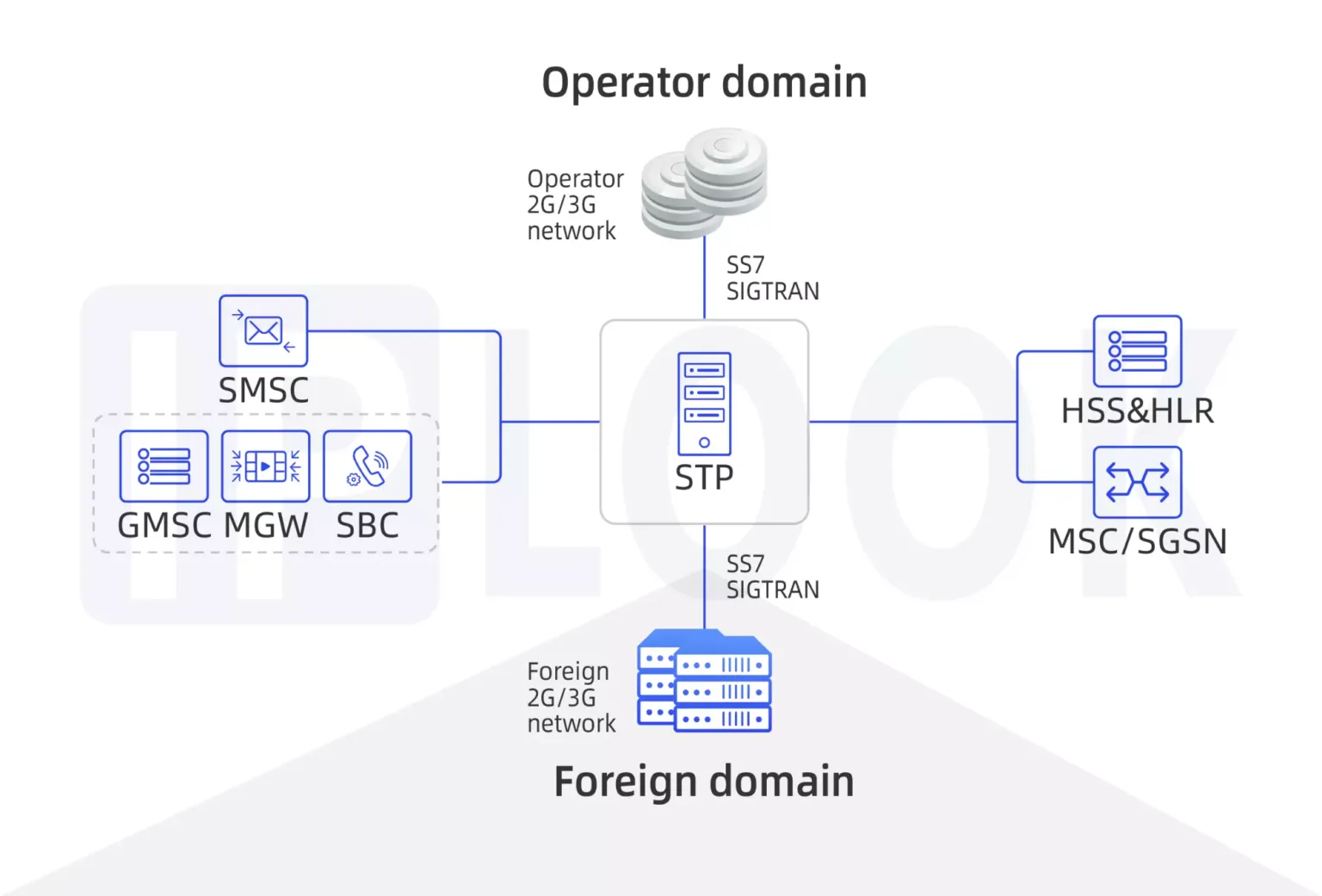
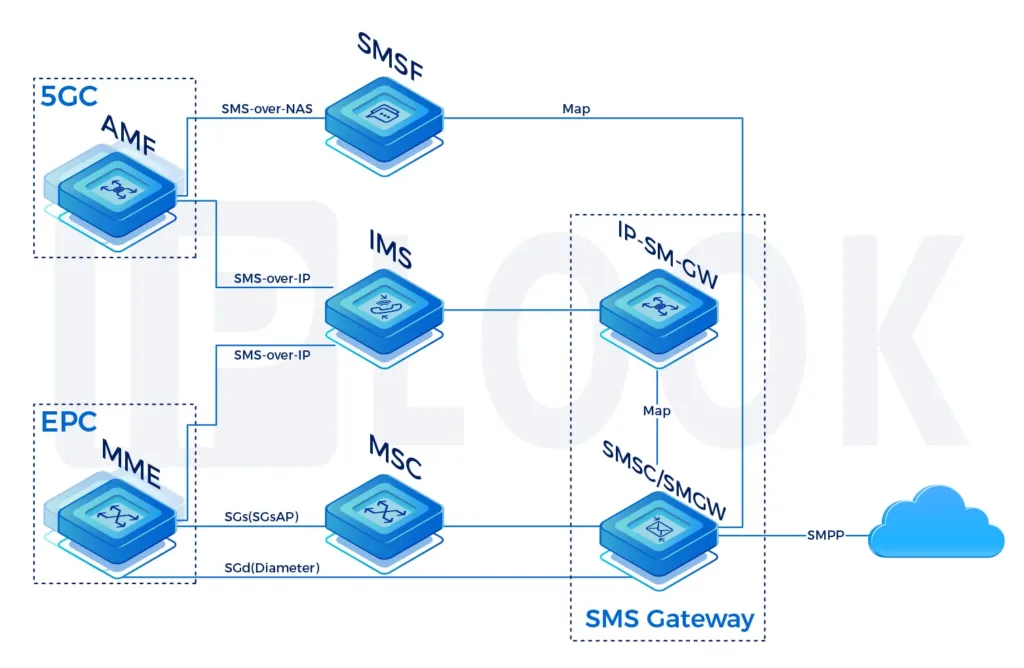
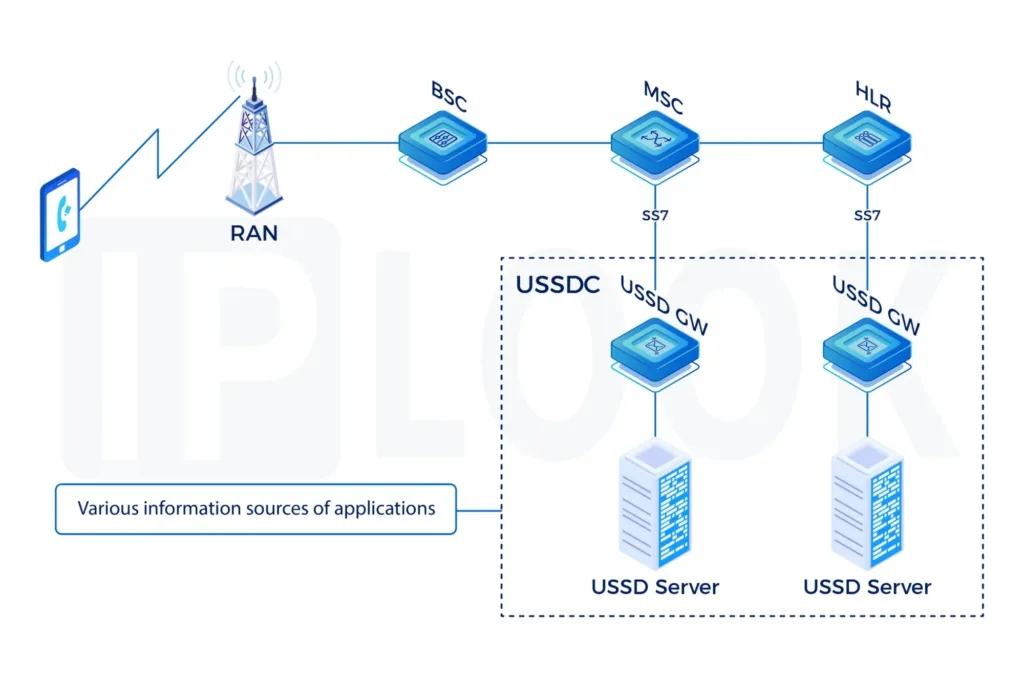
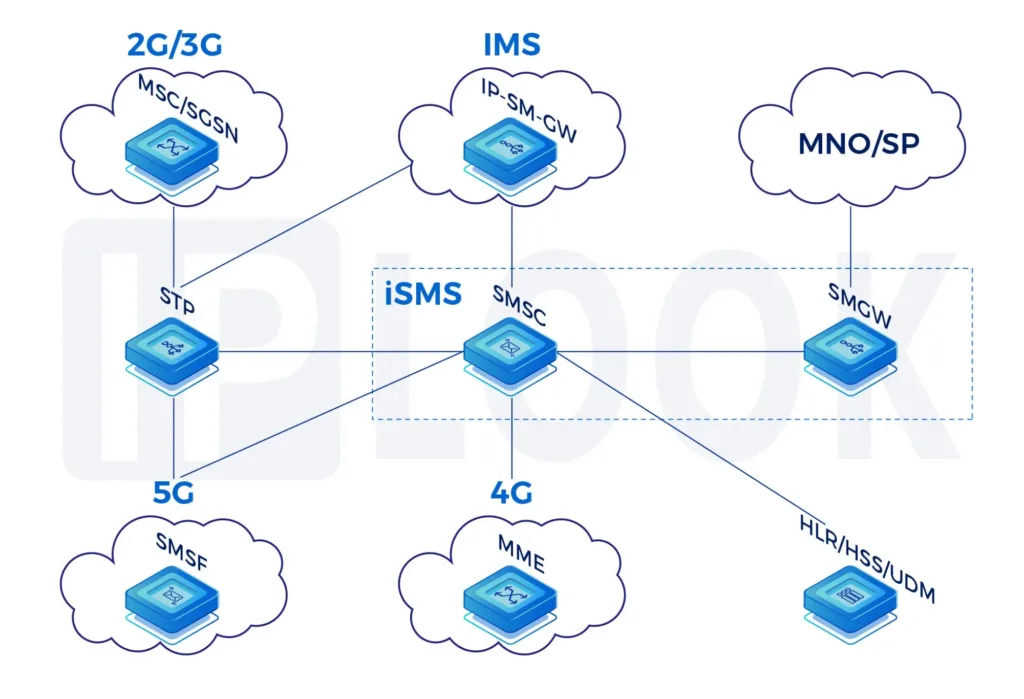
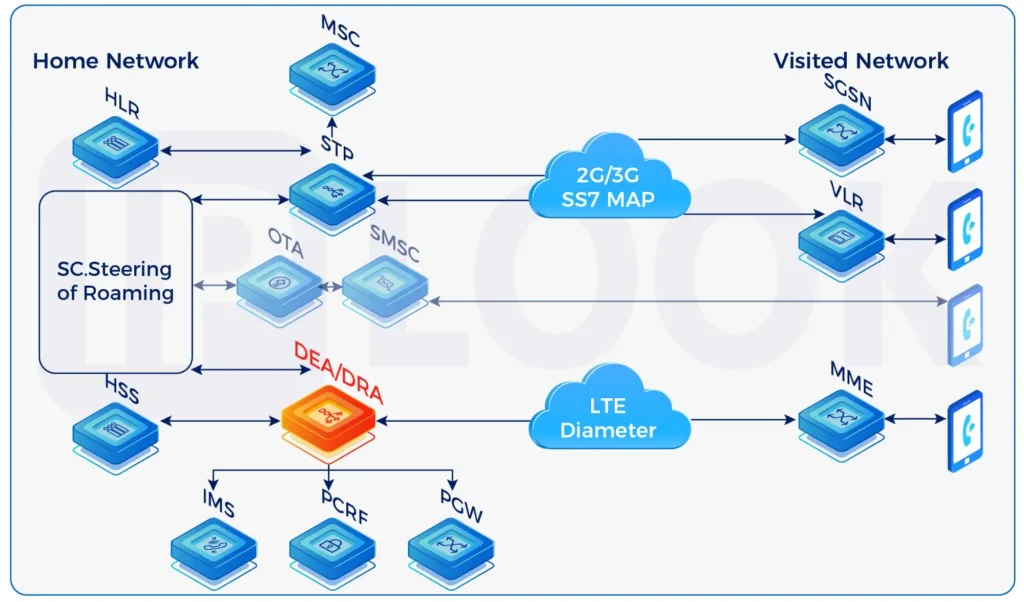
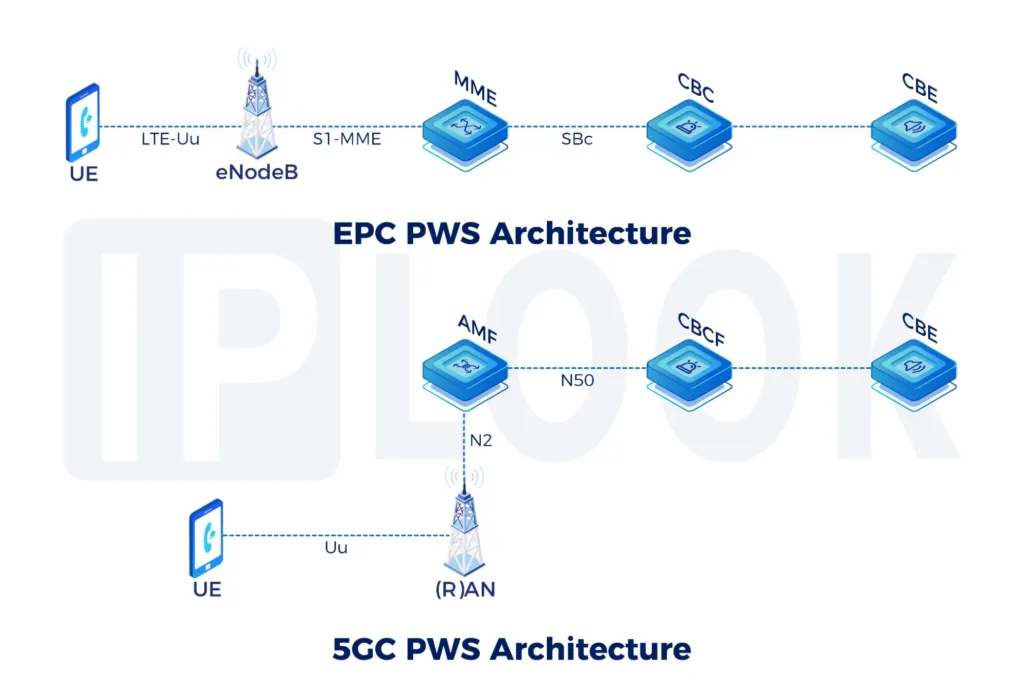
Signal Transfer Point(STP)
A Signal Transfer Point(STP) is used in an SS7 or CC7 network. The STPs transfer SS7 messages between interconnected nodes (signaling endpoints) based on information contained in the SS7 address fields. Typical SEPs include service switching points (SSPs) and service control points (SCPs). The STP is connected to adjacent SEPs and STPs via signaling links.
STP supports any-to-any signaling connectivity between SS7 via IP SIGTRAN interfaces for maximum network integration flexibility. The STP offers all the standard features and functionality expected of an STP solution, including Gateway Screening and Global Title Translation, while also offering extended capabilities and features such as Signaling Gateway and Point Code Emulation.
Key Benefits

Flexible Pricing
Deployment scale and future growth
Scalability
Support Multiple Point Codes, Capability Point Codes

Redundancy
1+1 Redundancy Mated Pair 1+1 & Mated Pair

Gateway Screening
MTP, SCCP, Called/Calling Party Enables first line firewall capability

Cloud Deployment
Delivered as a Virtual Network Function (VNF) in Cloud

Migration Enablement
Enabling rapid migration from standard STP platforms
IPLOOK's STP Multi-Layer Routing Support
- IPLOOK STP/DRA products follow RFC, 3GPP, IFC and relevant protocol specifications, which could deliver all the standard features and functionality expected of STP/DRA solution while also offering extended capability and features.
- Our STP is a comprehensive solution for intelligent routing of SS7 signaling traffic in 2G and 3G networks. It is part of IPLOOK’s integrated solution portfolio for converged, multi-protocol signaling across 2G/3G, 4G and 5G (SS7, Diameter, HTTP, SIP and more). The STP offers a future-proof choice, with major benefits compared to traditional STP products.
- The IPLOOK STP offers a scalable architecture with flexible pricing designed to meet budget expectations, deployment scale and future growth.
Features
SCCP
- NOA, etc.
- GT, PC, SSN
- Called and Calling
- Variant Translation ETSI to ANSI
- Routing on incoming SCCP label
- Outgoing SCCP label manipulation
- Translate routing variant (GT > PC+SN, etc.)
Redundancy:
- Standby Redundancy – Passive Standby Software instance
- Mated Pair and Standby redundancy – Combination of the above
- Mated Pair Redundancy – 2 Independent STP' s configured with a C Link
- Architecture is designed around client requirements and overall dimensioning
Support RFC 6733 Standard Routing
Support for SIGTRAN standards M3UA
- MTP3/SCCP/TCAP
MTP, SCCP, MAP routing
- Highly flexible and high throughput routing engine for MTP, SCCP and MAP routing
Operation and Management
- Web Client
- Command Line Interface
Routing Management
- Routing rules based on:
- Peer Role
- Application ID
- Contents of AVP