Our High-Performing Core Network
Fully virtualizable on VMware, K8S, Docker and OpenStack containers
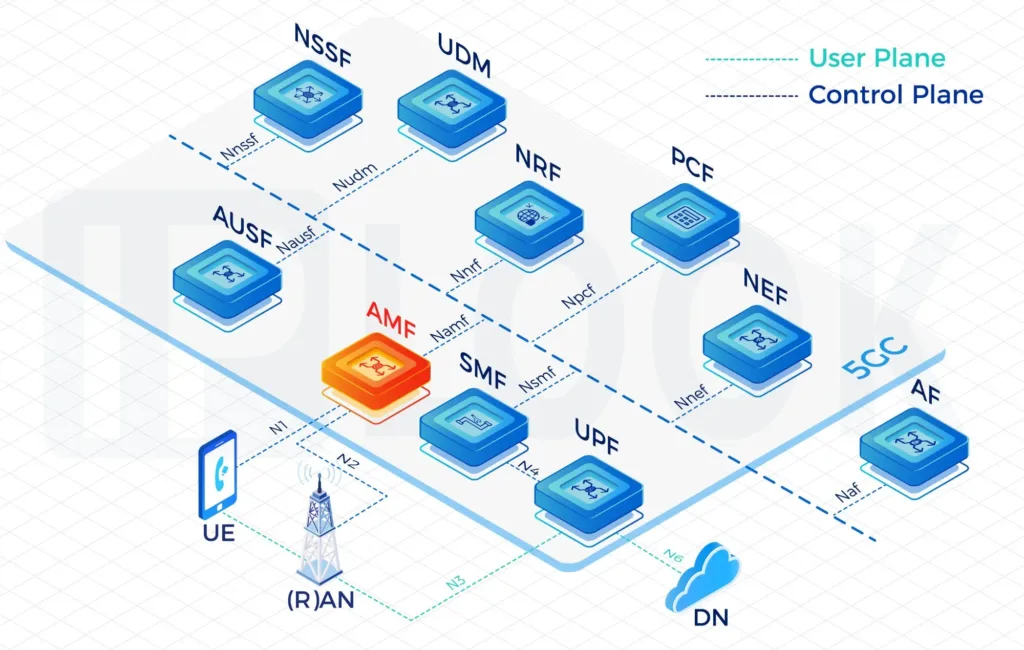
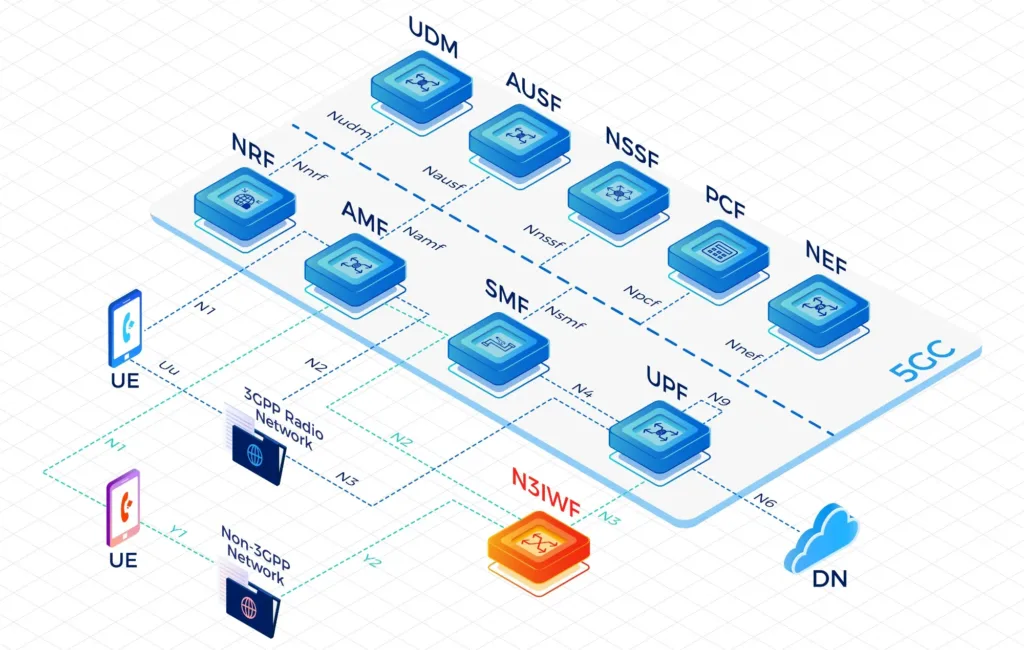
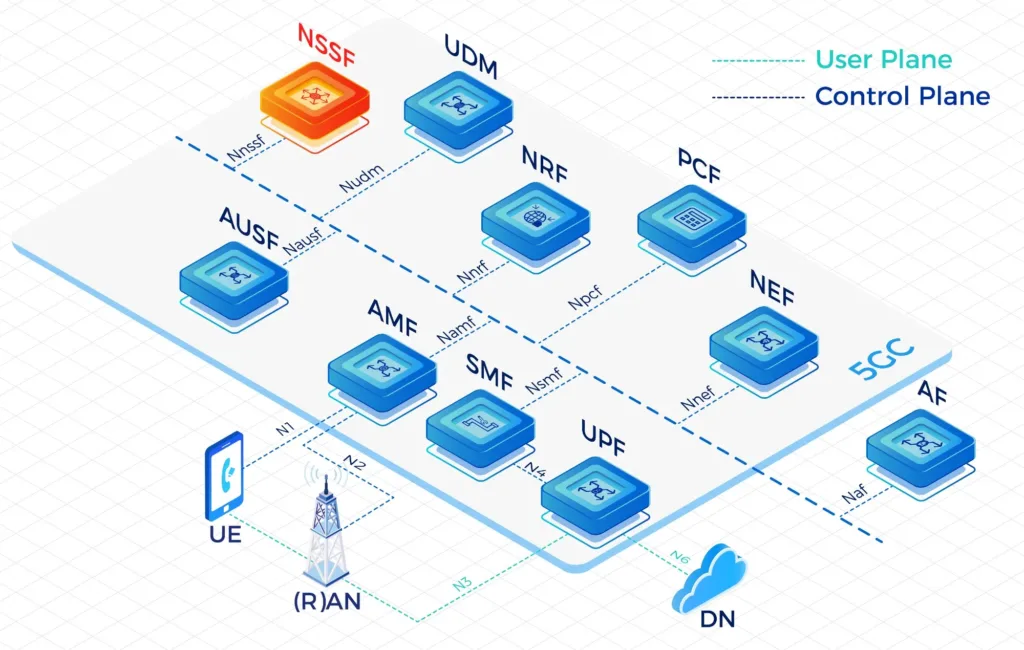
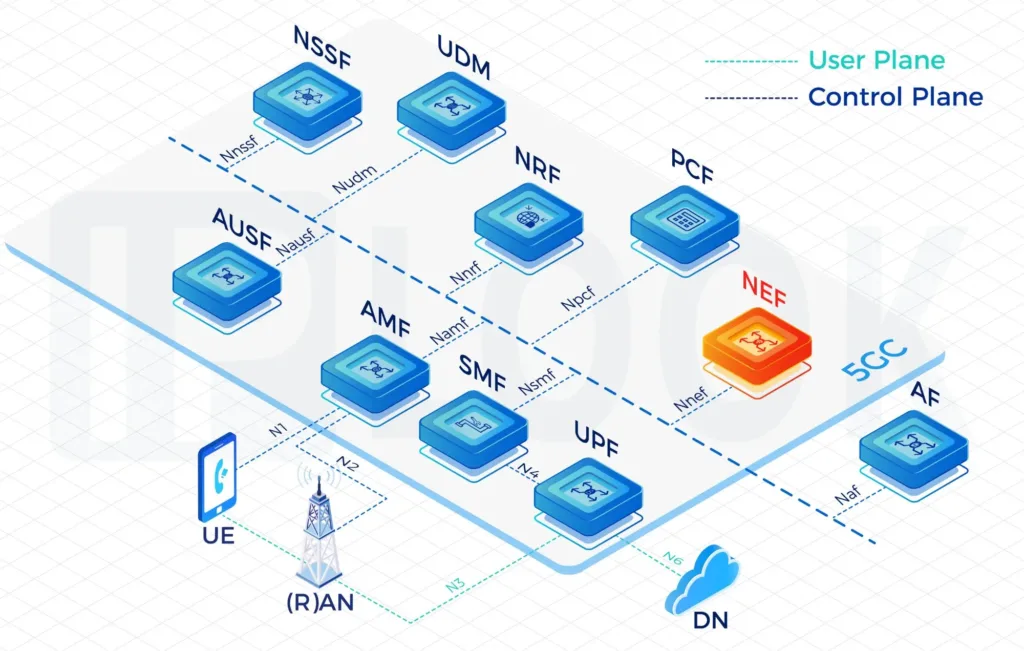
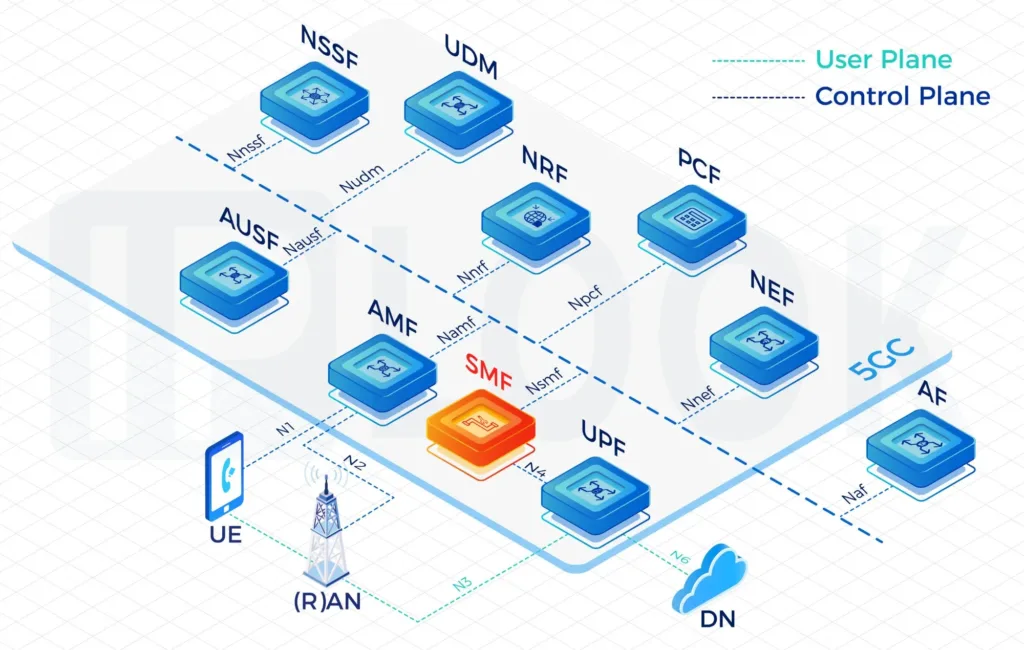
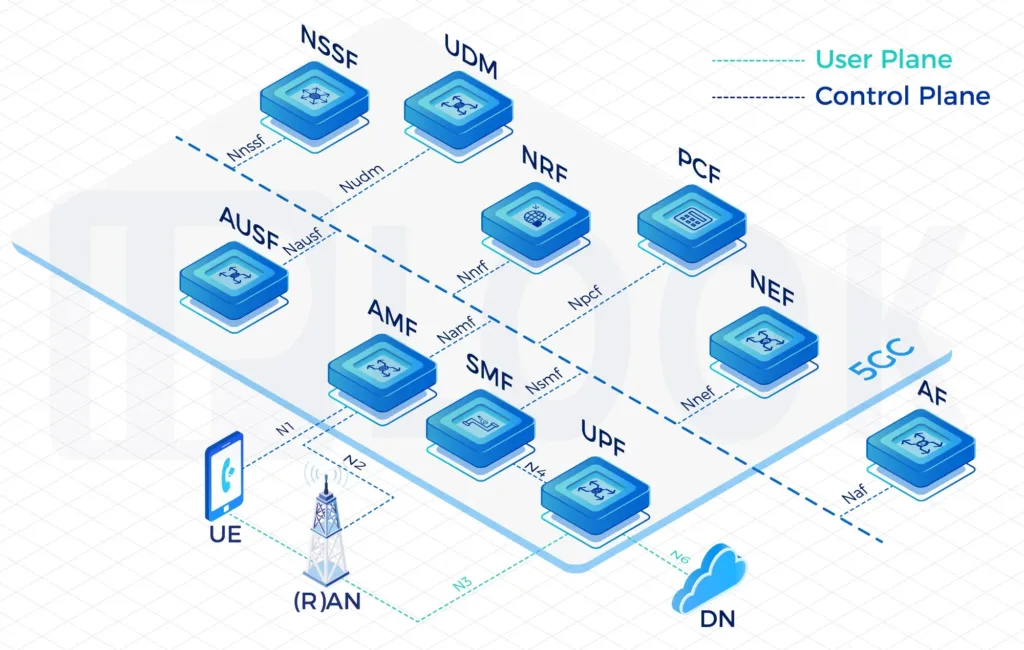
Access and Mobility Management Function(AMF)
AMF terminates the control plane of different access networks onto the 5G Core Network(5GC) and control which UEs can access the 5GC to exchange traffic with DNs. It also manages the mobility of UEs when they roam from one gNB to another for session continuity, whenever possible.
Key Benefits

Converged EPC MME and 5GC AMF core network function

Perfect compatibility with third-party core network elements

Deployed on X86 COTS server, NFV platform and Cloud

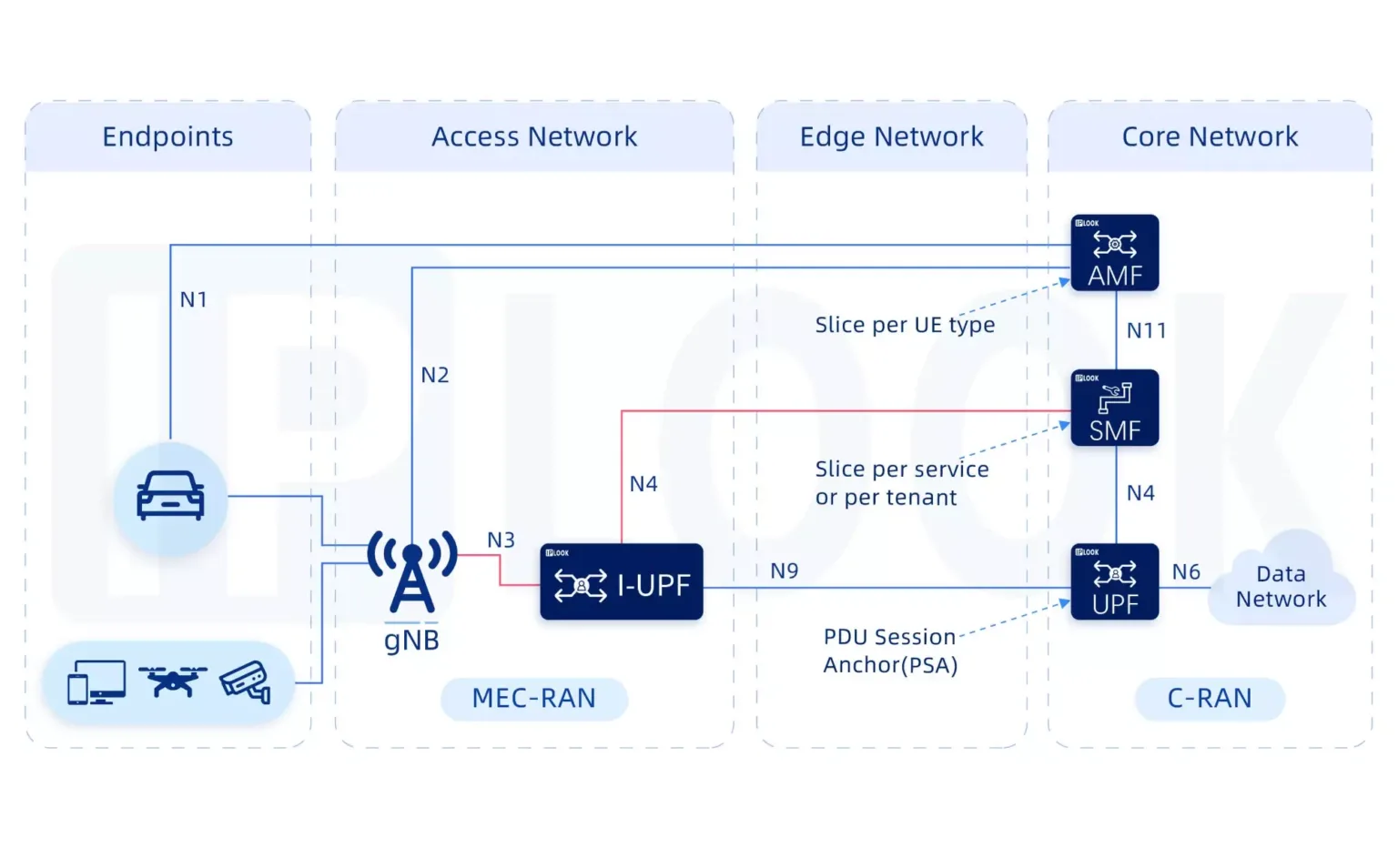
Enabled for centralized or distributed data centers
IPLOOK's 5GC AMF
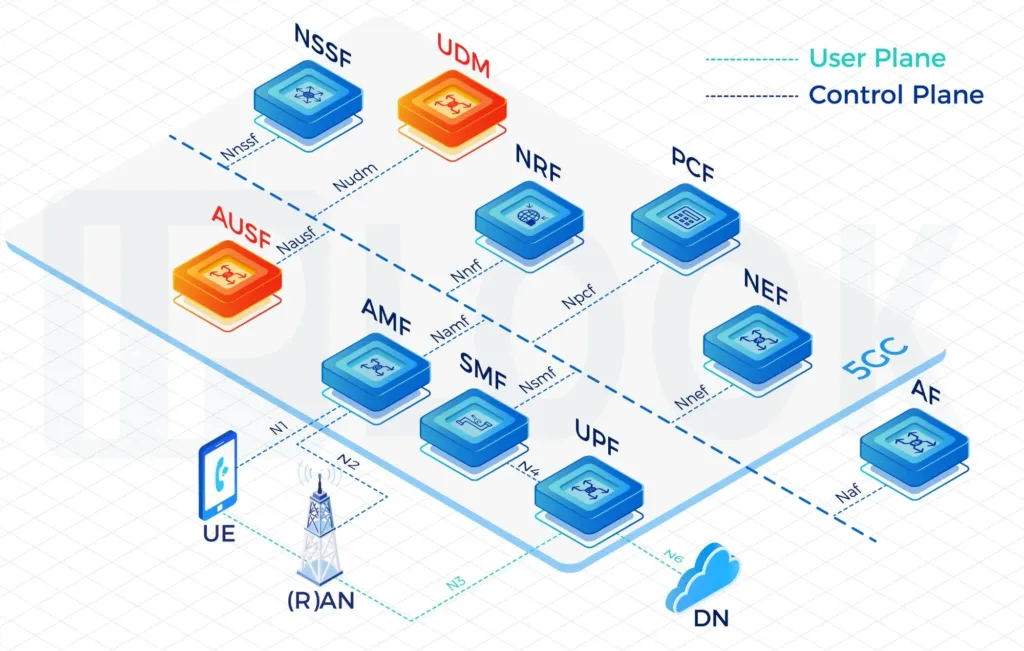
- IPLOOK 5GC AMF supports registration management, access control and mobility management function for all 3GPP accesses as well as non-3GPP accesses such as WLAN. AMF also receives mobility related policies from PCF (e.g. mobility restrictions) and forwards them to the UE. AMF fully supports 4G interoperability with the interface to 4G EPC MME node.
- Assuming the responsible for mobility management, the AMF is in charge for managing handovers between gNodeB’s (gNB’s), within the Next Generation Radio Access Network (NG-RAN). Formally referred to as an X2 handover, in 5G it is termed an Xn handover. This represents the updated reference interface application protocol (XnAP) employed between gNB base stations, which is defined within the 3GPP’s Technical Specification (TS) 38.423.
Features
Comply to 3GPP R15/R16 Standards
Interface Function
- S6a/S6d Interface
- N1 Interface
- N2 Interface
- N8 Interface
- N11 Interface
- N12 Interface
- N14 Interface
- N15 Interface
- N22 Interface
- N26 Interface
- Web Server
Mobility Management
- Registration
- UE-initiated Deregistration
- AMF-initiated Deregistration
- UDM-initiated Deregistration
- Mobility Registration Update
- Periodic Registration Update
- UE triggered Service Request
- Network Triggered Service Request(Paging)
- RAN Configuration Update
- N2 release procedure
- Xn-based handover
- Intra AMF N2-based handover
- Inter AMF N2-based handover
- Location Report
- UE Configuration Update
- AMF Configuration Update
- 5GS to EPS Handover(Idle State)
- EPS to 5GS Handover(Idle State)
- 5GS to EPS Handover(Connect State)
- EPS bearer ID allocation
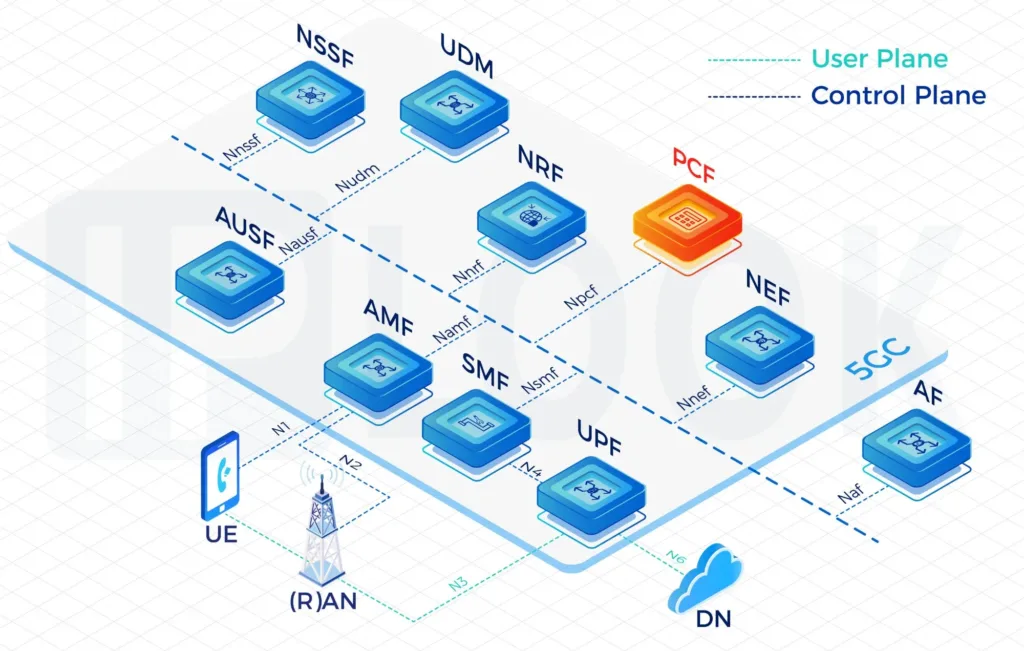
- AM Policy Control
- UE Policy Control
- MICO Mode
- AMF Reallocation
- Network Slice Selection
Element Management System(EMS) supported
Session Management
- PDU session establishment
- PDU session modification
- PDU session release
Operation and Maintenance
- KPI Management
- Fault Management
- Log Management
- Configuration Management
- License Management
- CLI
- Remote Operation and Maintenance
- Telnet
- Stelnet
- SFTP
- Daylight Saving Time
- Online Support
- Online Loading
- SSH
- Availability
Security Management
- NAS Security Mode Command
- The authentication and key agreement(5G AKA)
- User Identity Confidentiality
- GUTI Reallocation
- User Data and Signalling Confidentiality
Network Function Management
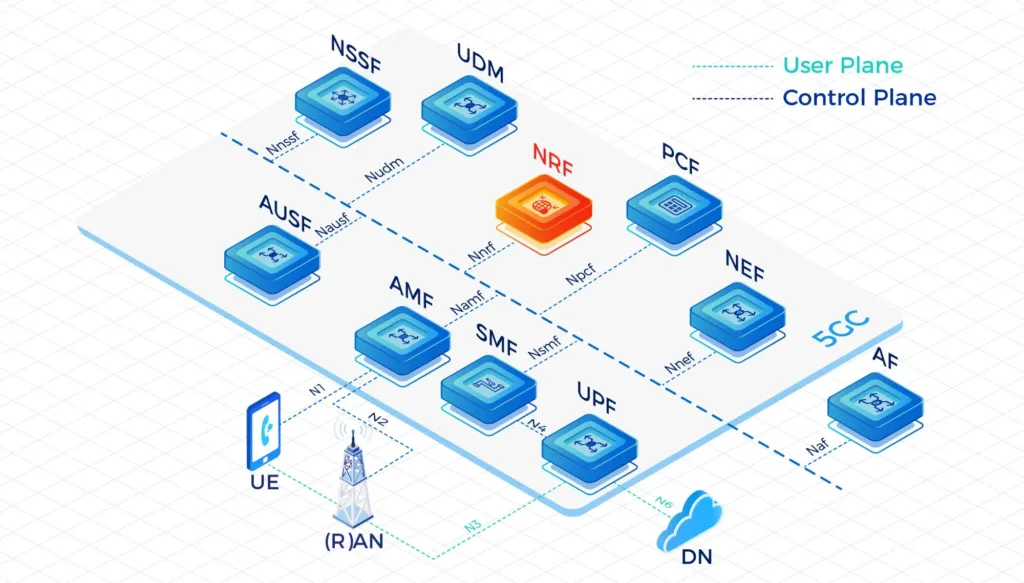
- NF Register
- NF Subscription
- NF Deregister
- Access Token
Open Northbound interface and graphical web based management interface
- API
- RESTful