Our High-Performing Core Network
Fully virtualizable on VMware, K8S, Docker and OpenStack containers
5G Core Network(5GC)
5G Core Network(5GC) holds a key role in realizing the full potential of 5G services. Without 5GC, fully-fledged NR services cannot be obtained. 5G NSA deployment leaning on traditional LTE network and EPC allows for a quick launch of 5G services, but also hinders the realization of 5G’ s full potential.
Base on Service Based Architecture(SBA), in 5GC, a cloud native design is introduced to enable flexible scaling and upgrades.
Key Benefits

Supports VoNR/VoLTE/CSFB
Allow operators to meet a variety of voice application scenarios
Flexible Deployment
Enable for centralized or distributed data centers

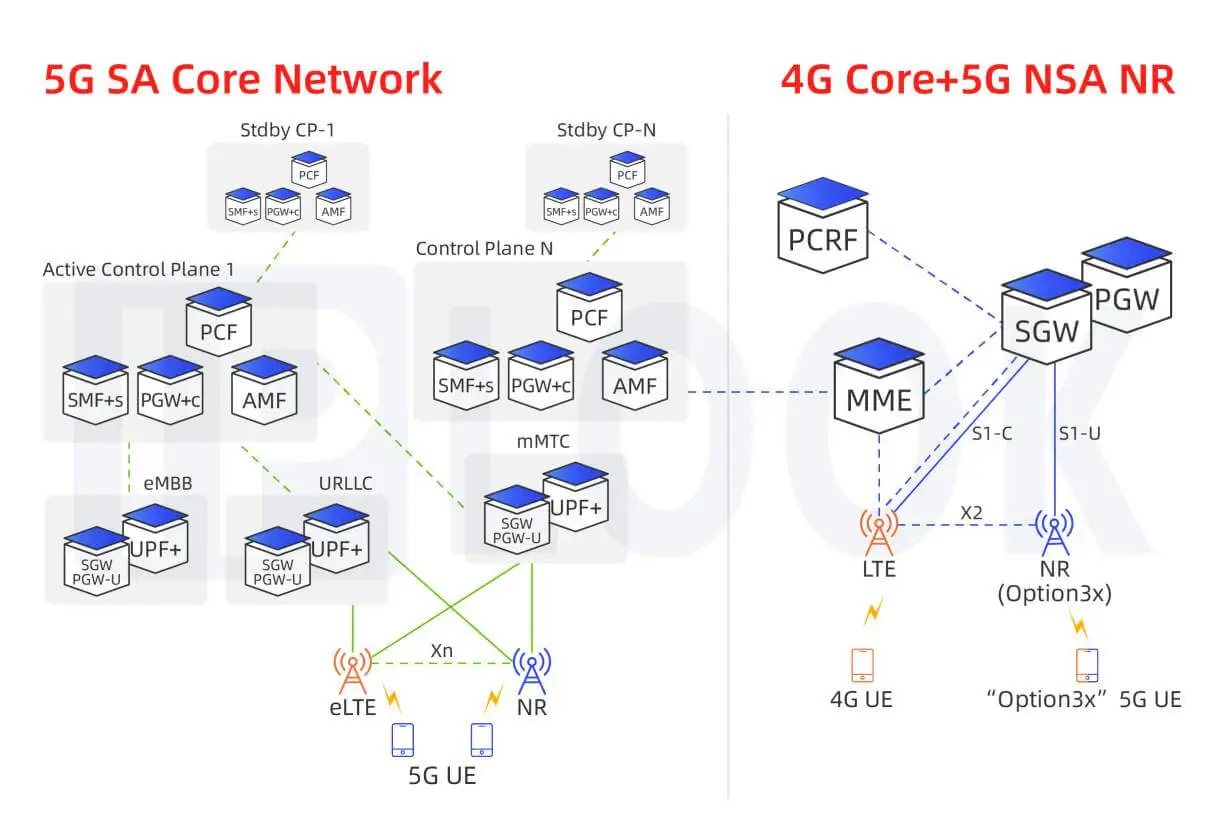
Virtualized, Cloud-Native Dual-Mode 5G Core
Support NSA/SA Networking

Fully standards based, multivendor solution
Supports End-to-End 5GC Slicing

3G/4G/5G Converged Core
Enable smooth handover among 3G, 4G and 5G

Full Stack capabilites
A complete core network portfolio, Simplify operators' network structure

High scalable
Enable to deploy on Cloud Platform such as AWS and Azure

Enable more granular end-to-end management and control of traffic flows and applications
IPLOOK's Ultra 5G Core Network
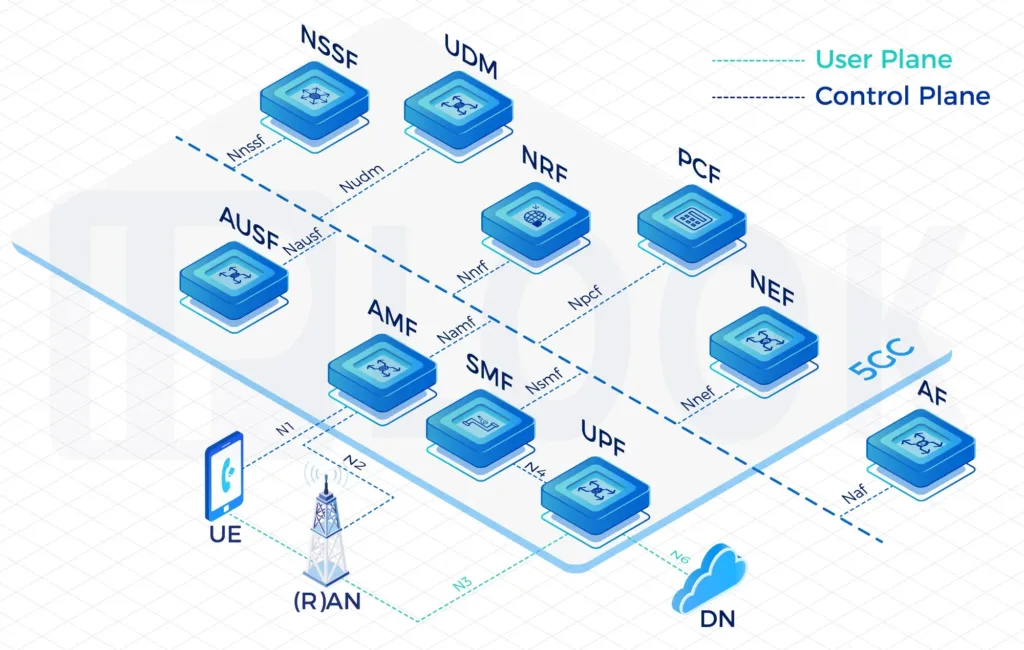
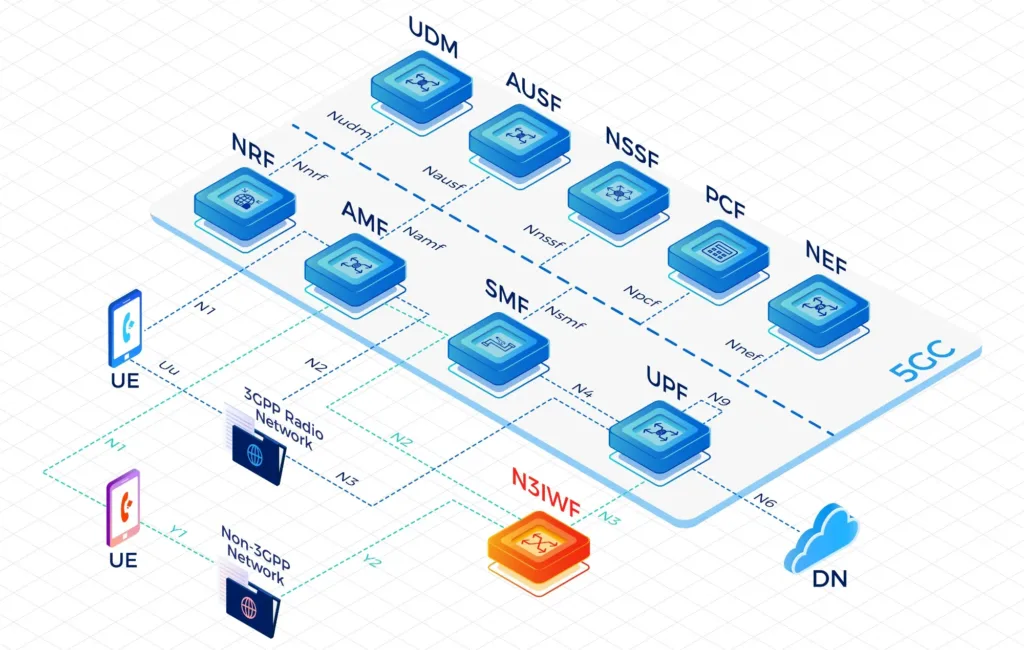
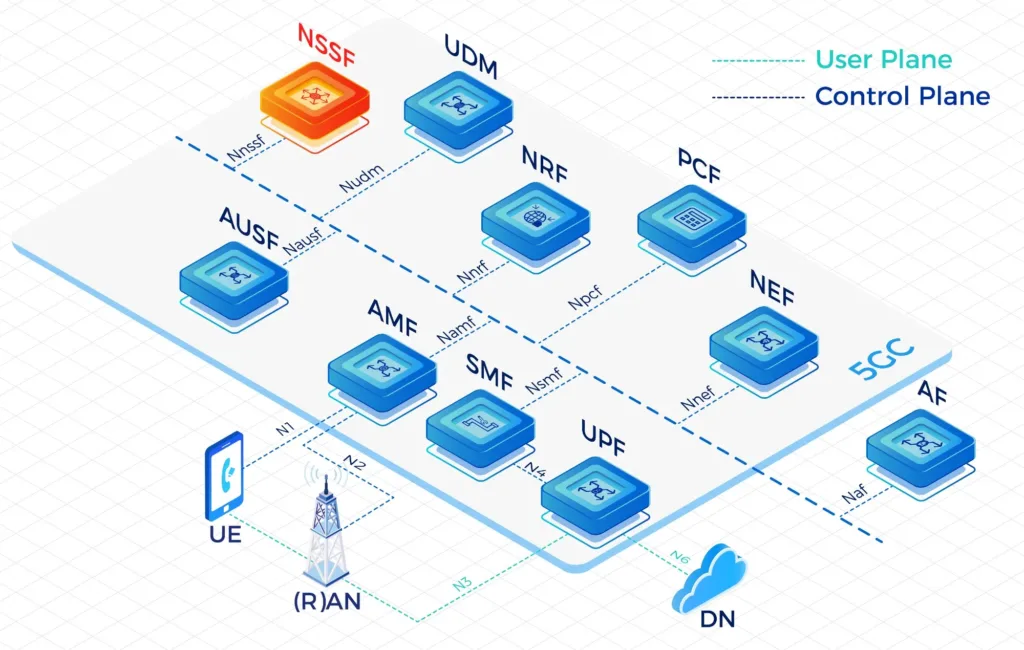
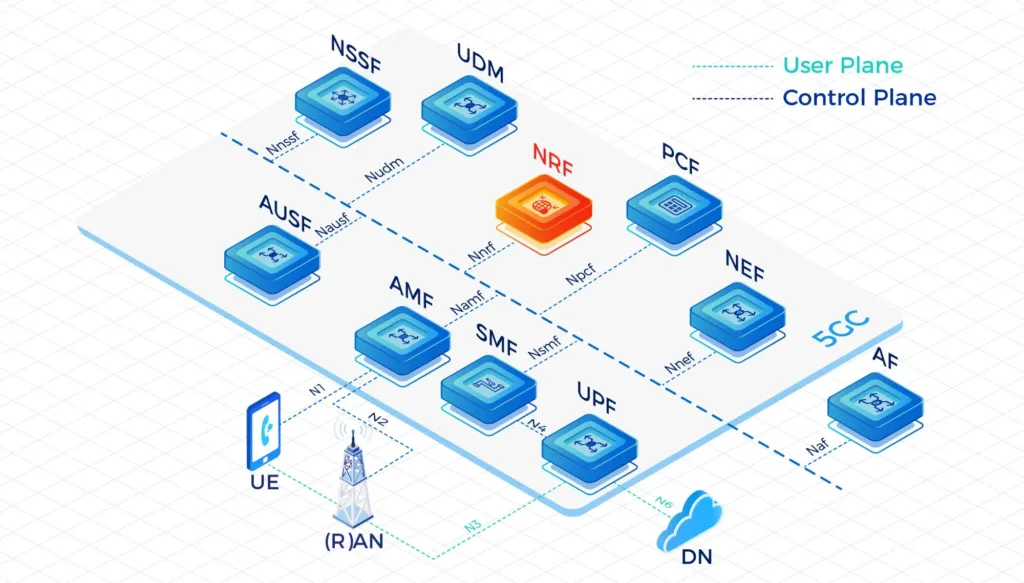
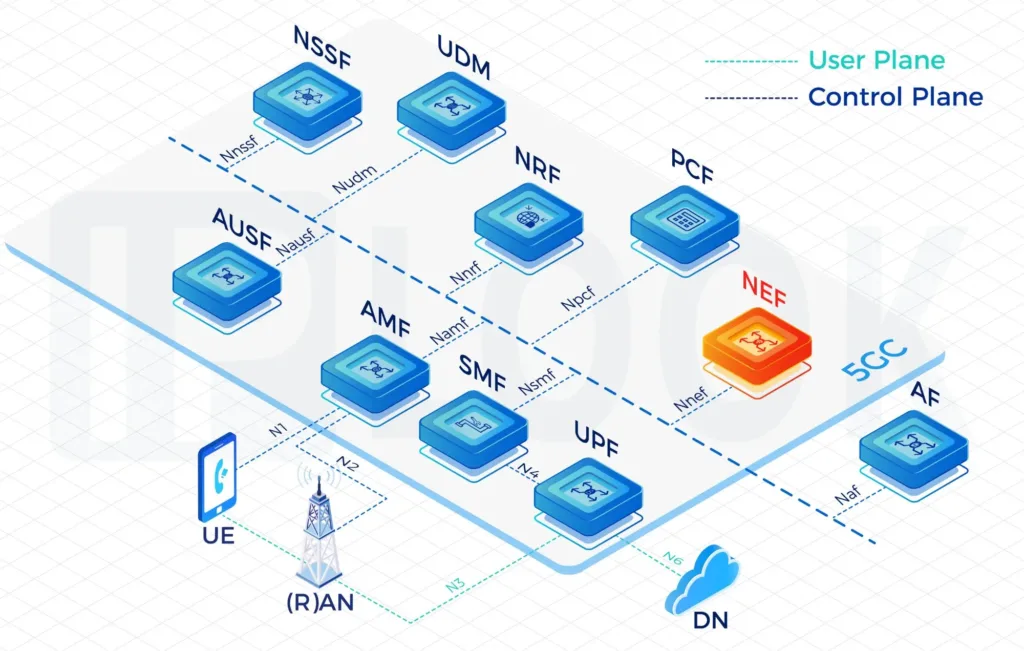
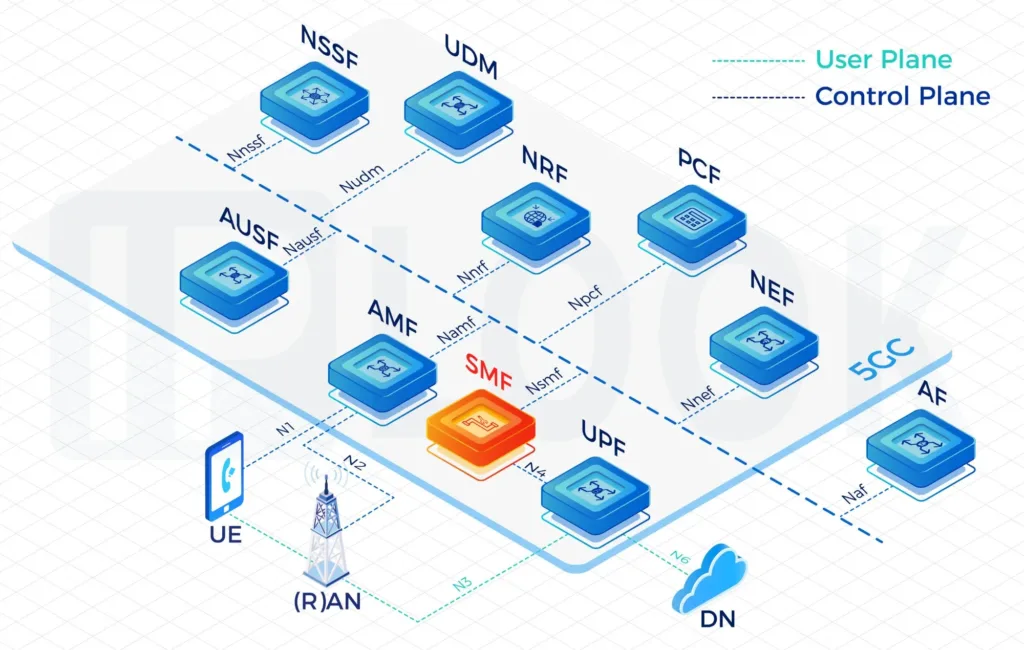
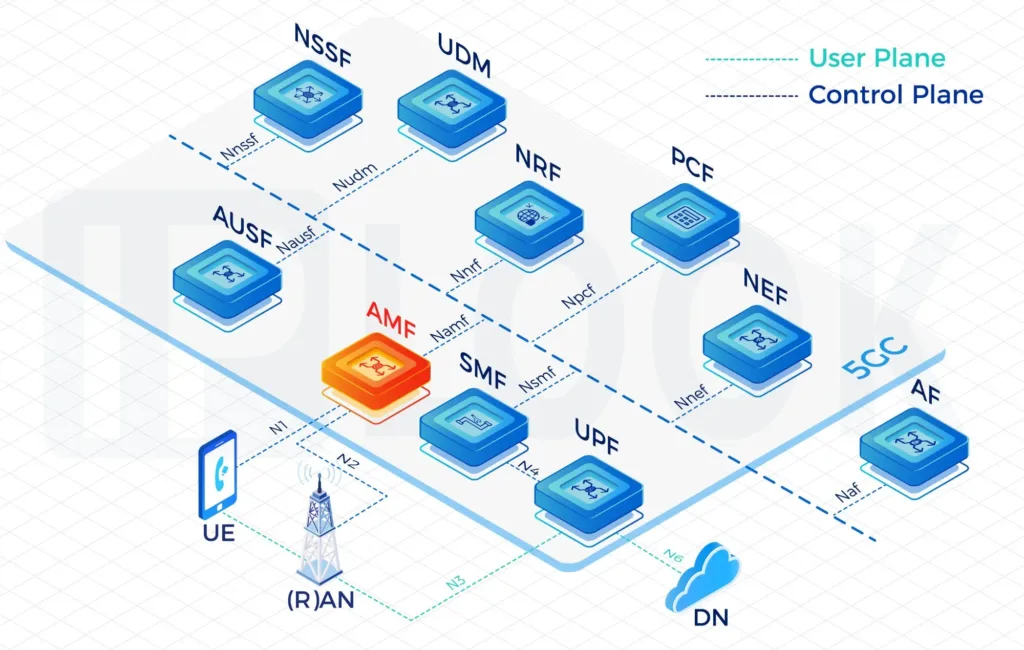
- IPLOOK’s 5GC includes the elements: UPF, AUSF, UDM, AMF, SMF, PCF, NSSF, NRF, NEF.
- Highly compact, IPLOOK 5GC can be implemented on low end COTS servers, or can utilize available CPU capacity in a radio by embedding directly into available CPU cores within the radio itself. It can also be containerized for deployment on an NFV platform.
- IPLOOK 5GC has higher compatibility and will be upgraded to support 3G and 4G user access. Users can register for 3G/4G/ 5G networks, thus ensuring a smooth upgrade to 5G for existing 3G/4G users.
- We enable 5G services for Service Providers, Systems Integrators, Enterprises and Government Organizations while optimally leveraging investments of existing networks and systems, at price levels which are significantly lower than the products of the established tier 1 vendors.
Features
Comply to 3GPP R15/R16 Standards
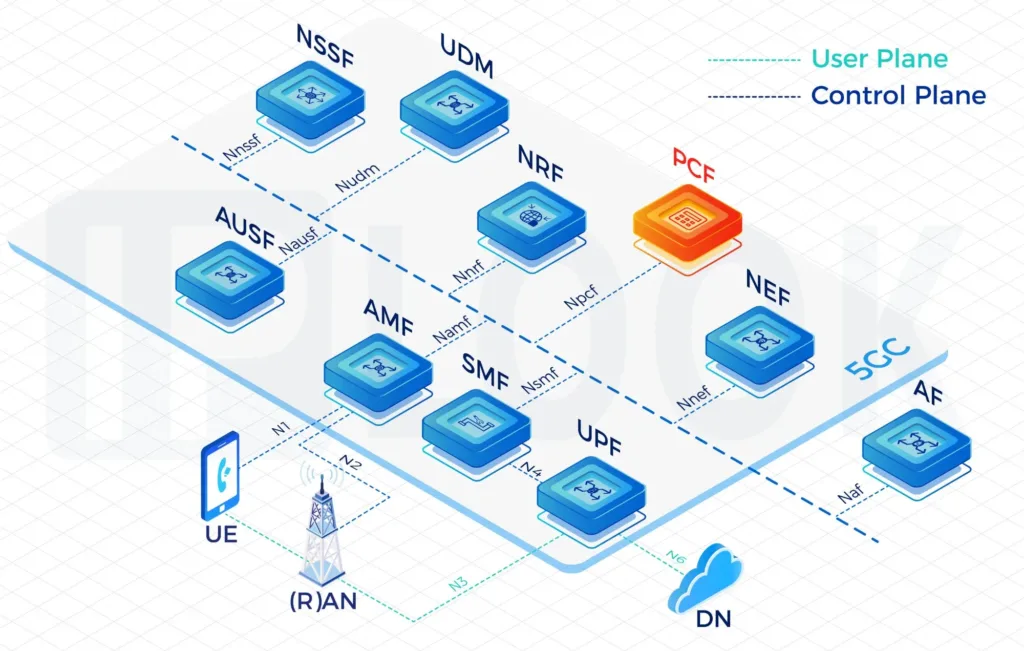
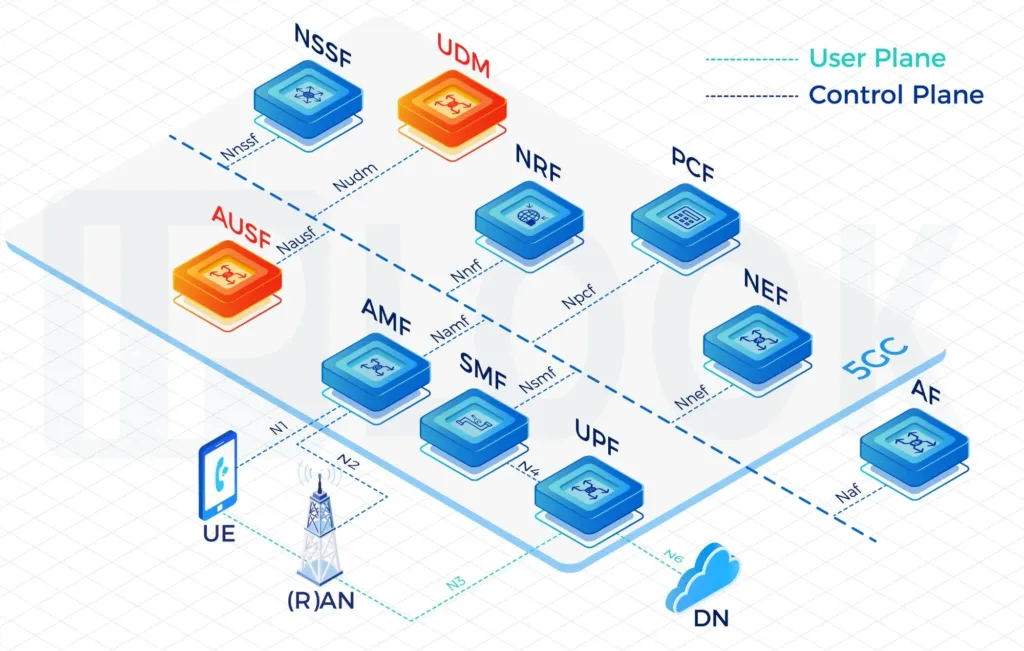
A Service Based Architecture (SBA): AMF, SMF, PCF, UPF, UDM, AUSF, NSSF, NRF, NEF Full Functions
- UPF: User Plane Function
- AMF: Access and Mobility Management Function
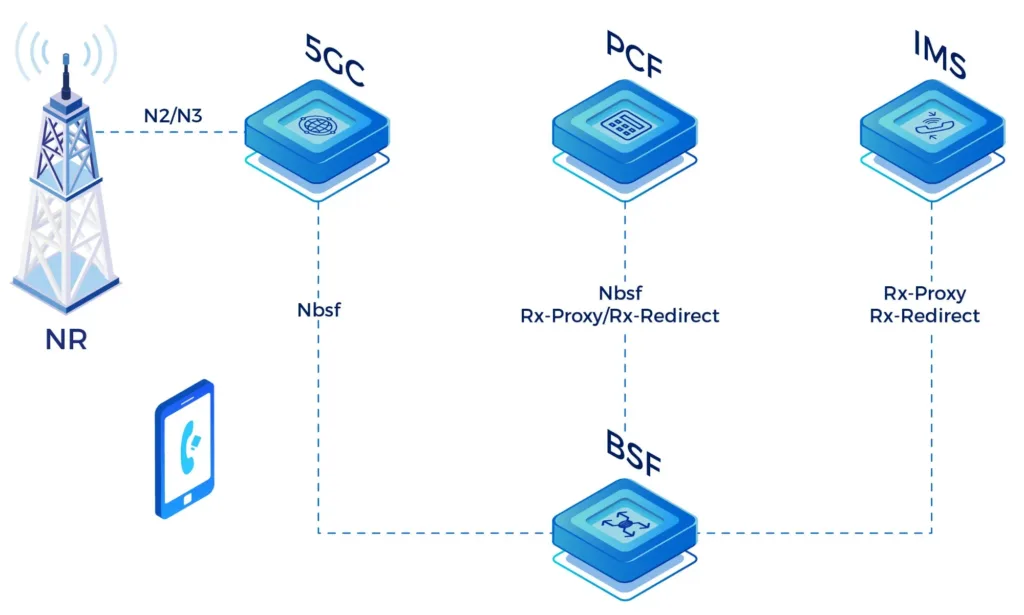
- BSF: Binding Support Function
- SMF: Session Management Function
- PCF: Policy Control Function
- UDM: Unified Data Management
- AUSF: Authentication Server Function
- NSSF: Network Slice Selection Function
- NRF: Network Repository Function
- NEF: Network Exposure Function
- NSSF: Network Slice Selection Function
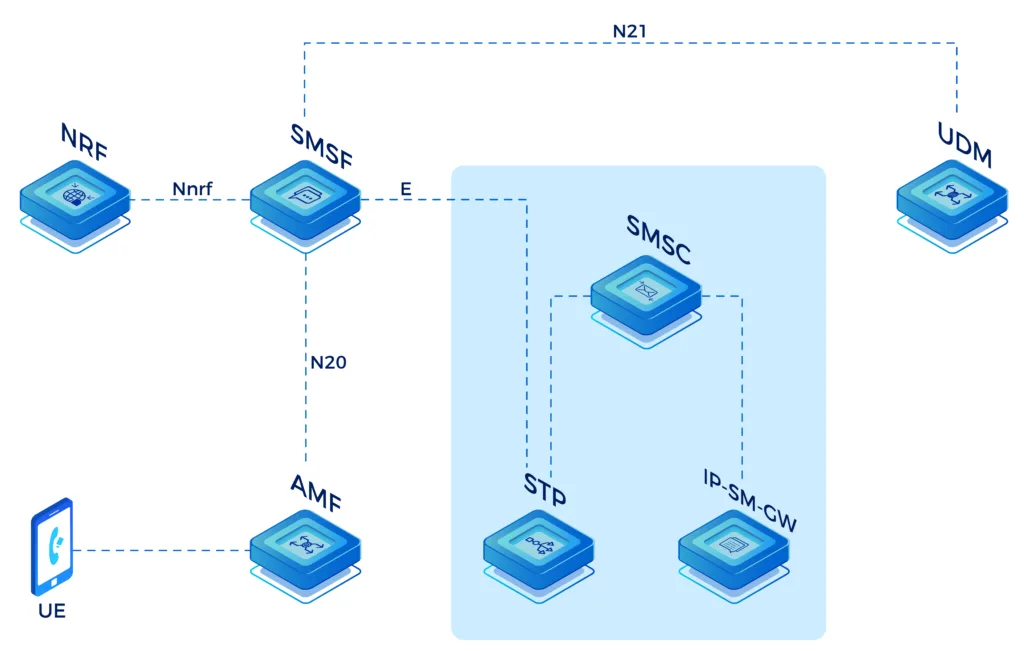
- SMSF: Short Message Service Function
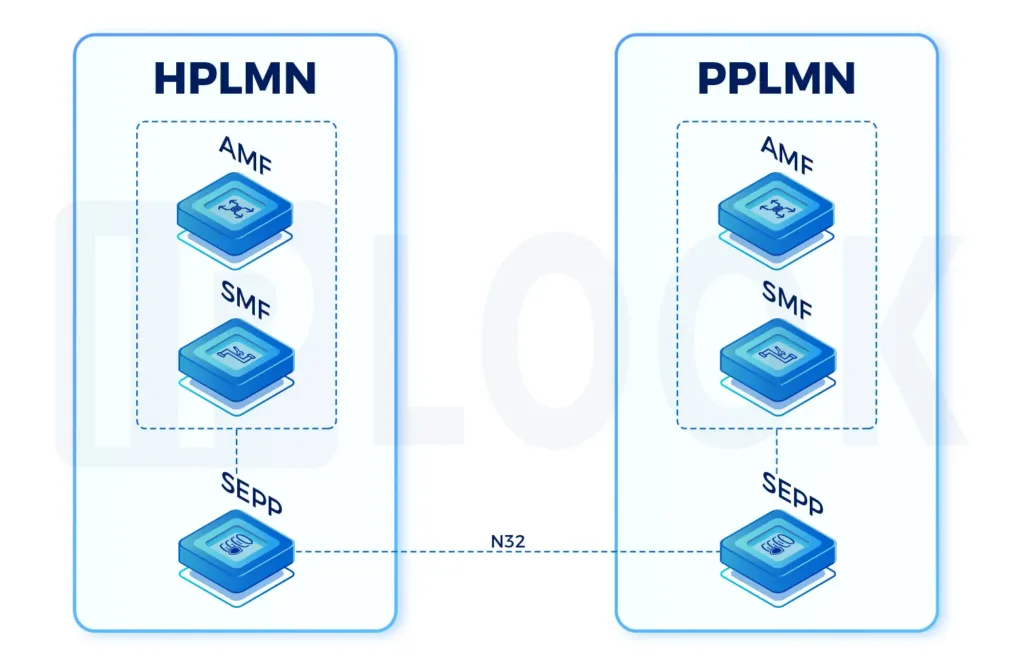
- SEPP:Security Edge Protection Proxy
- N3IWF:Non-3GPP InterWorking Function
The IoT with NR
- VoNR
5GC NFV Architecture
- Cloud Native
- Docker
Separate the User Plane (UP) functions from the Control Plane (CP) functions, allowing independent scalability, evolution and flexible deployments e.g. centralized location or distributed (remote) location
UPF Multi-Gbps support: 10GbE/25GbE/40GbE/100GbE
5GS interworking
- PGW-C/SMF
- PGW-U/UPF
- PCRF/PCF
- MME/AMF
- HLR/HSS/UDM/AUSF
- N26 interface