Our High-Performing Core Network
Fully virtualizable on VMware, K8S, Docker and OpenStack containers
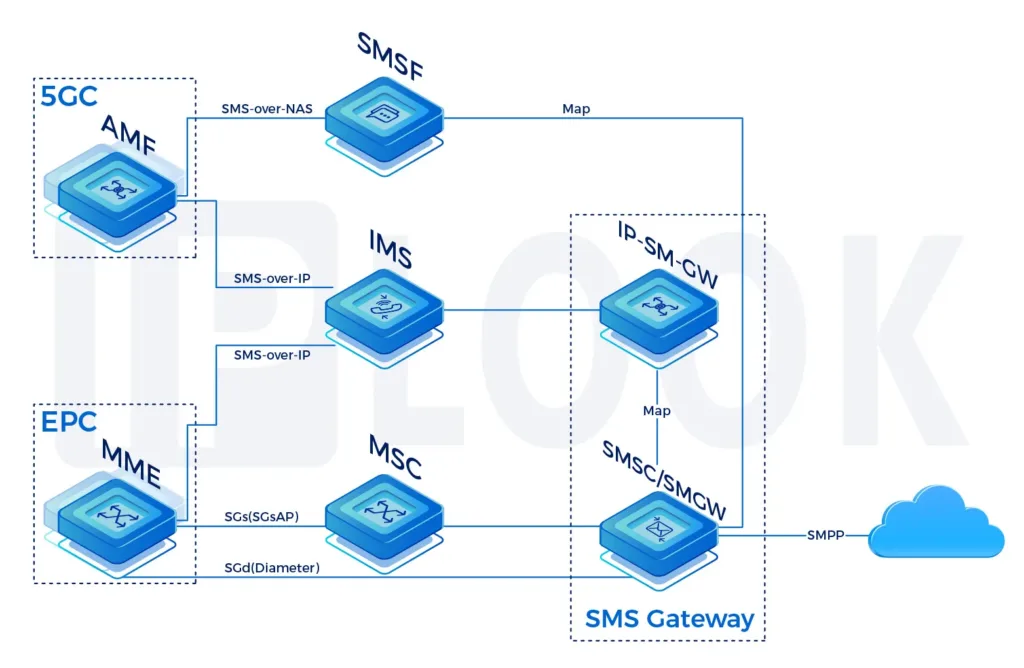
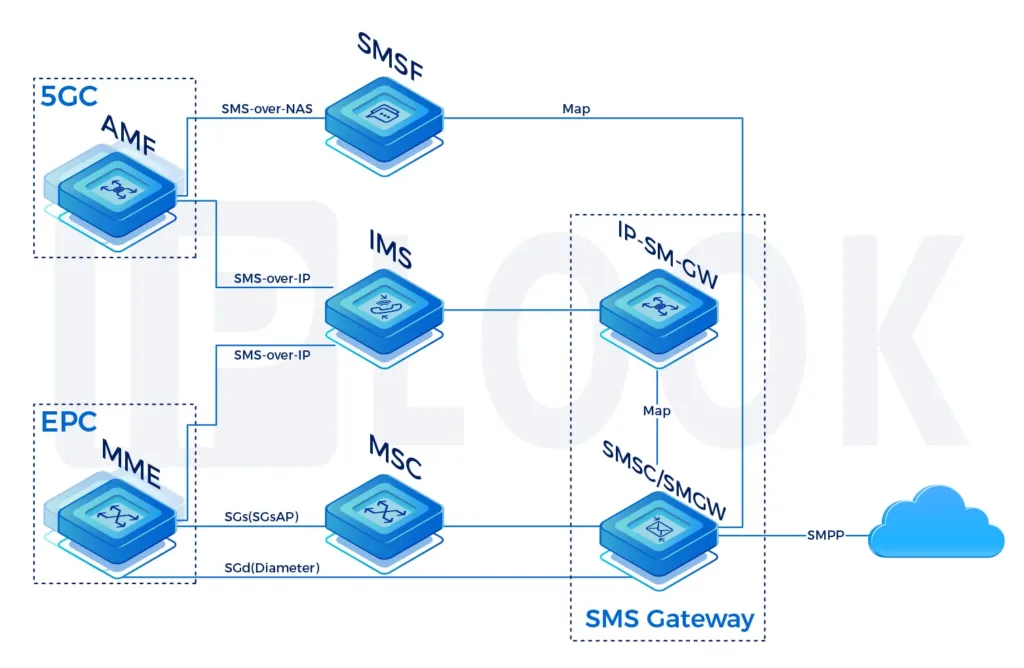
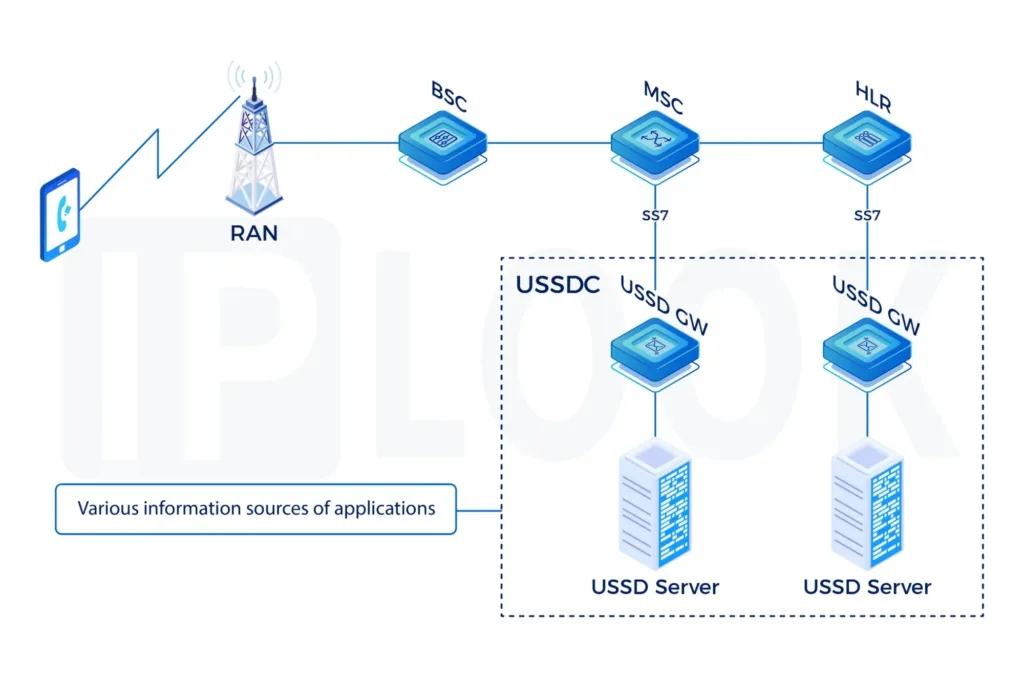
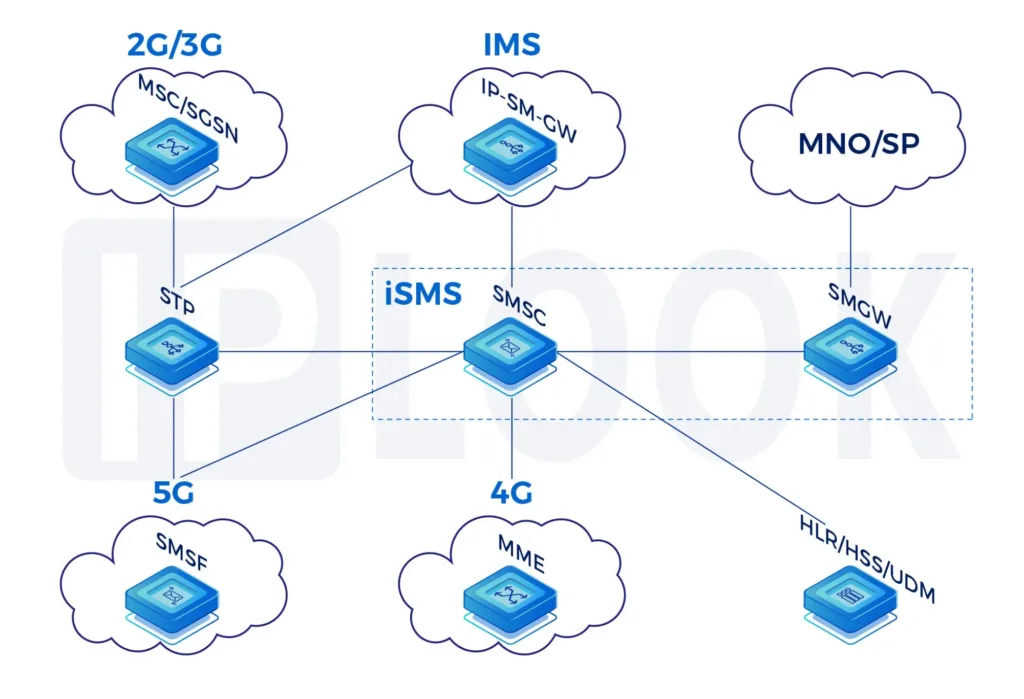
Mobile Signaling
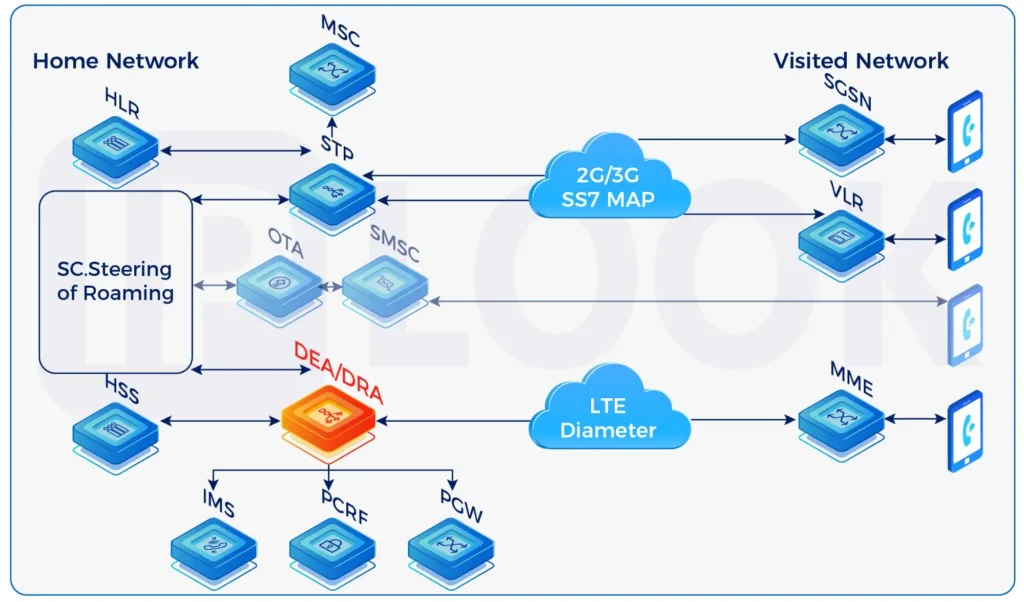
In Mobile Telecommunication, Signaling is the use of messages for controlling communications between the different elements within the Mobile Network. This may constitute an information exchange concerning the establishment and control of a telecommunication voice call, SMS, or data session.
Across all available Mobile Technologies different protocols are being used and require specific routing and security capabilities per domain which are listed below:
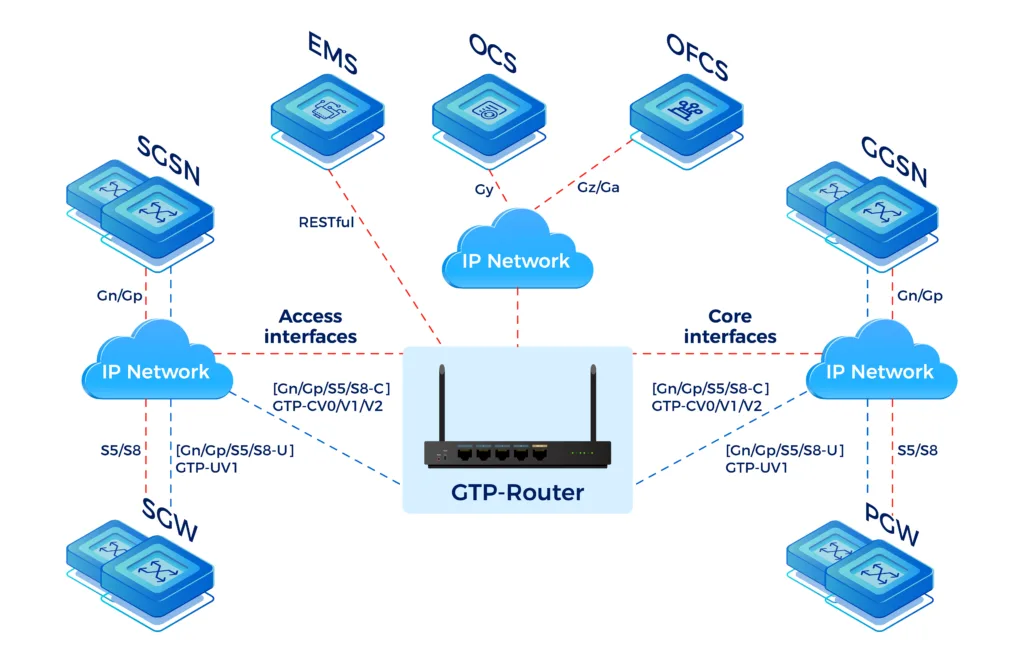
- 2G/3G network: SS7 Signaling MAP/CAP
- 4G/LTE network: Diameter Signaling
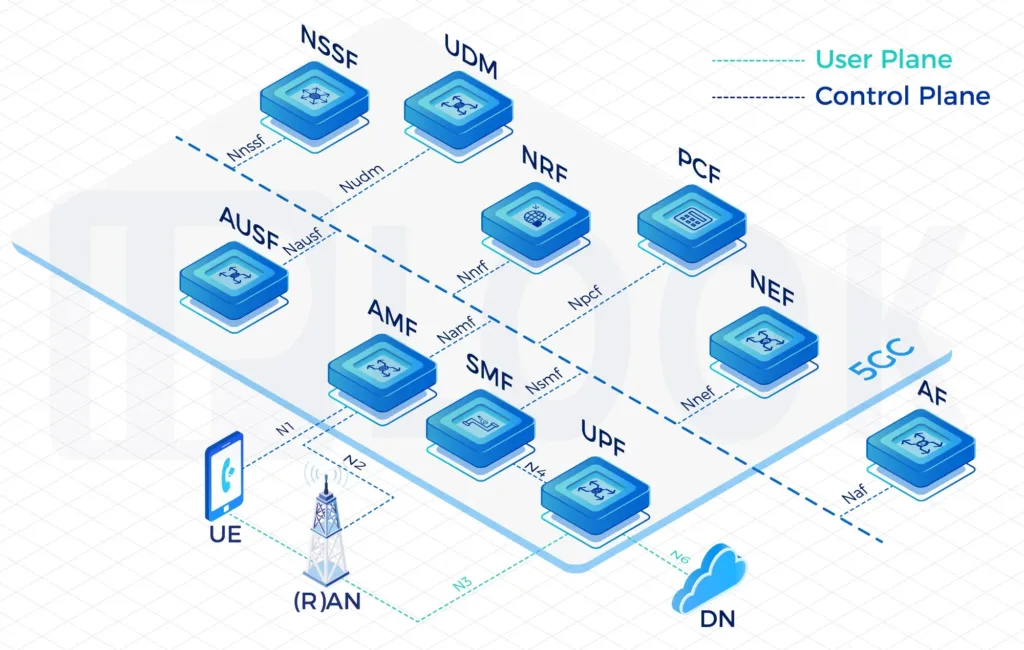
- 5G network: HTTP/2 Signaling
Target Applications

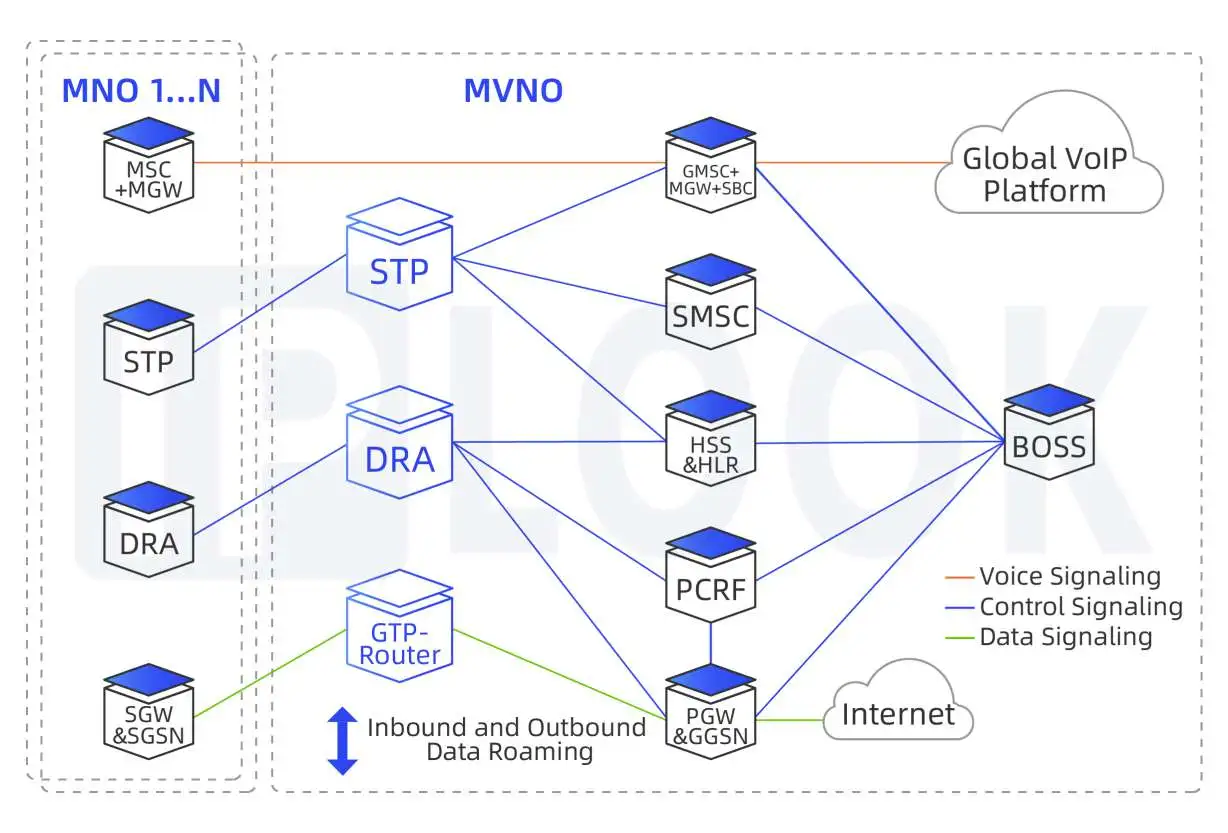
Diameter Router and Edge Agent in MNO and IPX Service Providers network
Front end of IMS/EPC platforms e.g. OCS, PCRF, AAA, HSS, SGSN for overloading

LTE Roaming Gateway

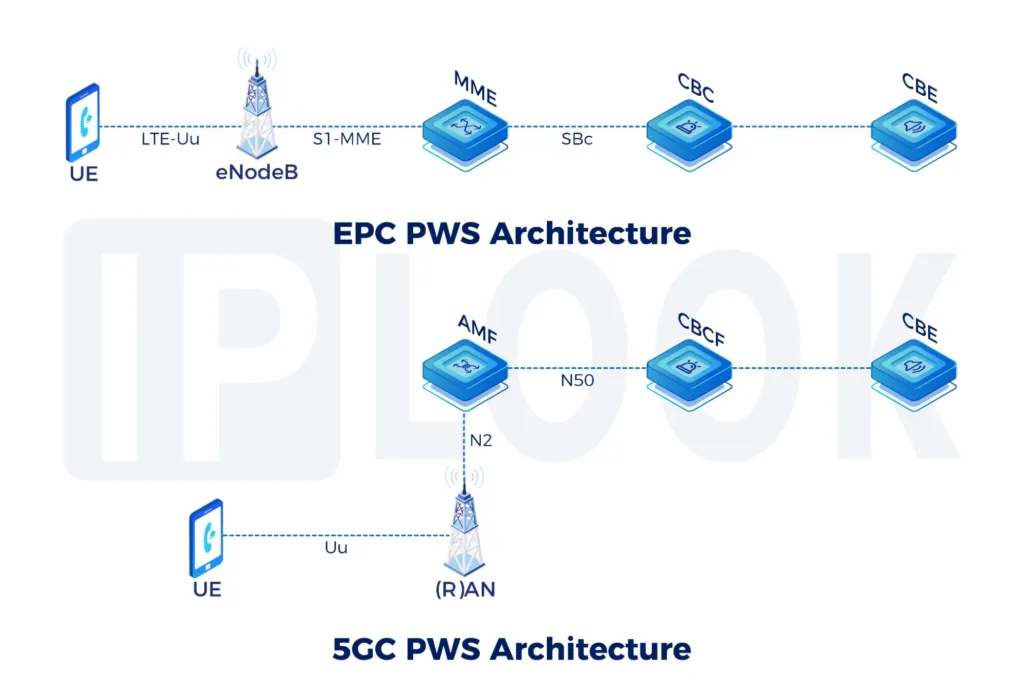
Inter Working Function between 2G/3G and 4G networks
IPLOOK's Mobile Signaling Solution Control your Mobile Network Communication
- It is important that within each Mobile Technology messages can be routed to a correct destination within the Home PLMN and for roaming purposes from and towards each Visited PLMN. Next to that, Protocol Interworking capabilities are vital to support technology fallback from 4G to 3G when losing coverage or to support Circuit Switched FallBack (CSFB).
- IPLOOK is a leading expert in intelligent routing and interworking solutions for 2G/3G, 4G/LTE, 5G, IMS, Fixed Wireless and M2M networks. We deliver Single Engine Signaling solutions and network applications for the telecommunications industry.
Features
SCCP routing
Support for SIGTRAN standards M3UA
- MTP3/SCCP/TCAP
Routing Management
- Routing rules based on:
- Peer Role
- Application ID
- Contents of AVP
Geo redundancy
- Standby Redundancy - Passive Standby Software instance
Operation and Management
- Web Client
- Command Line Interface