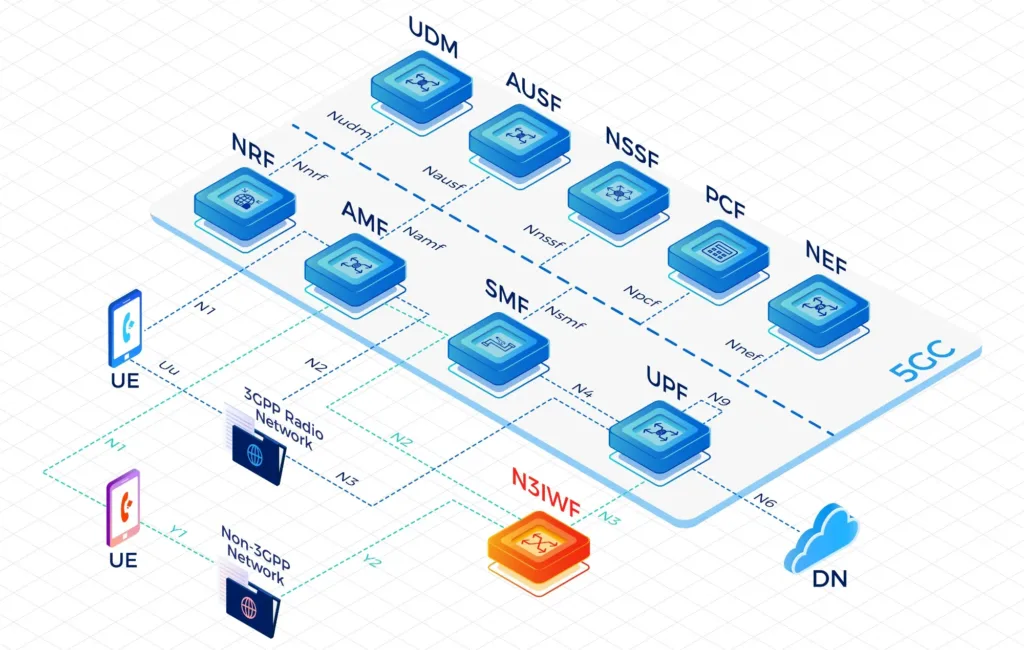
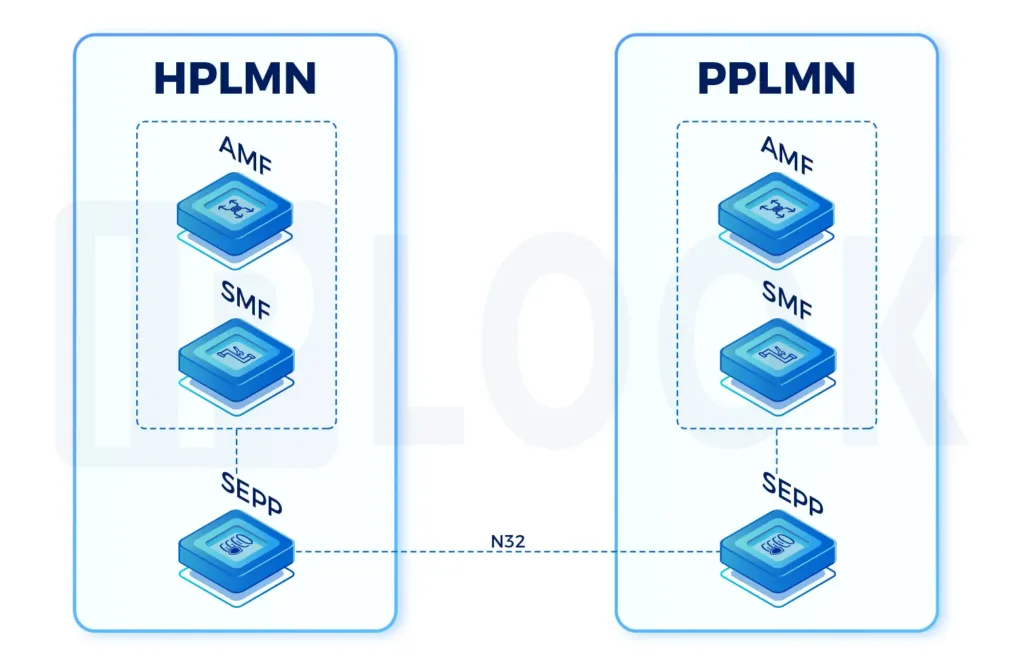
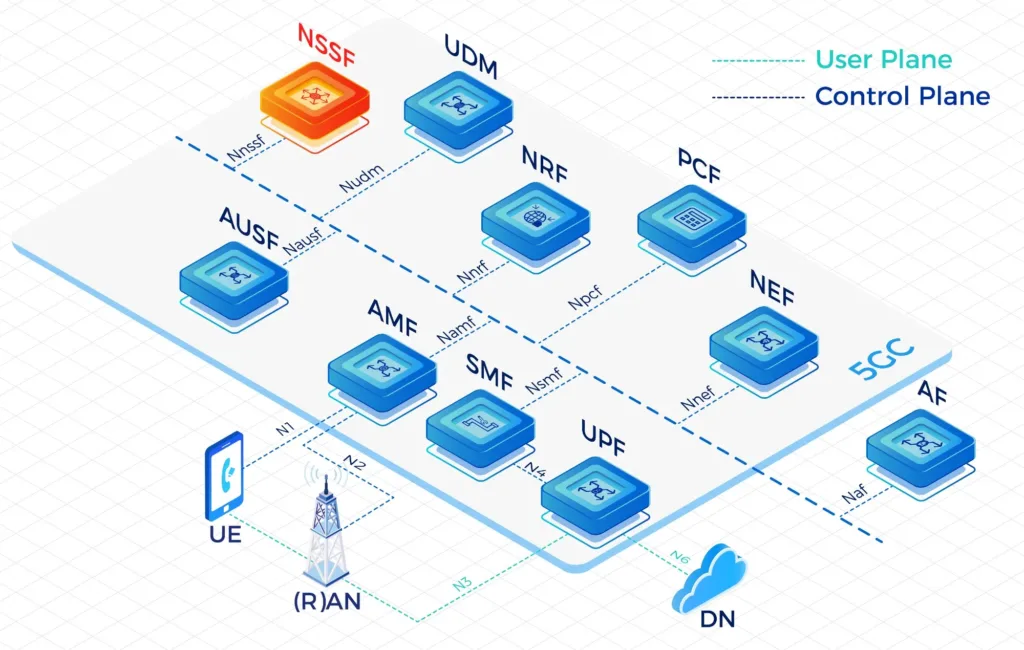
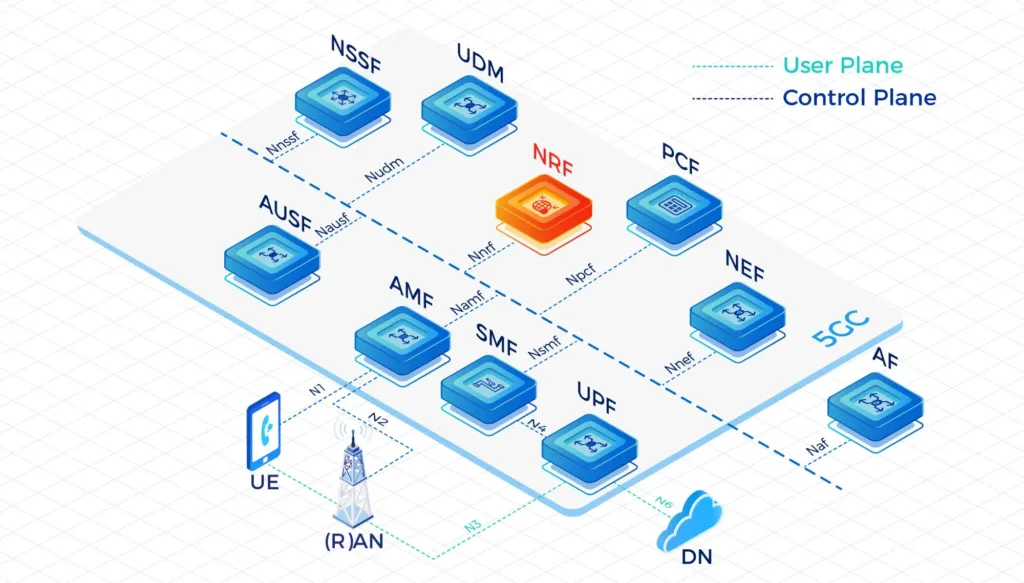
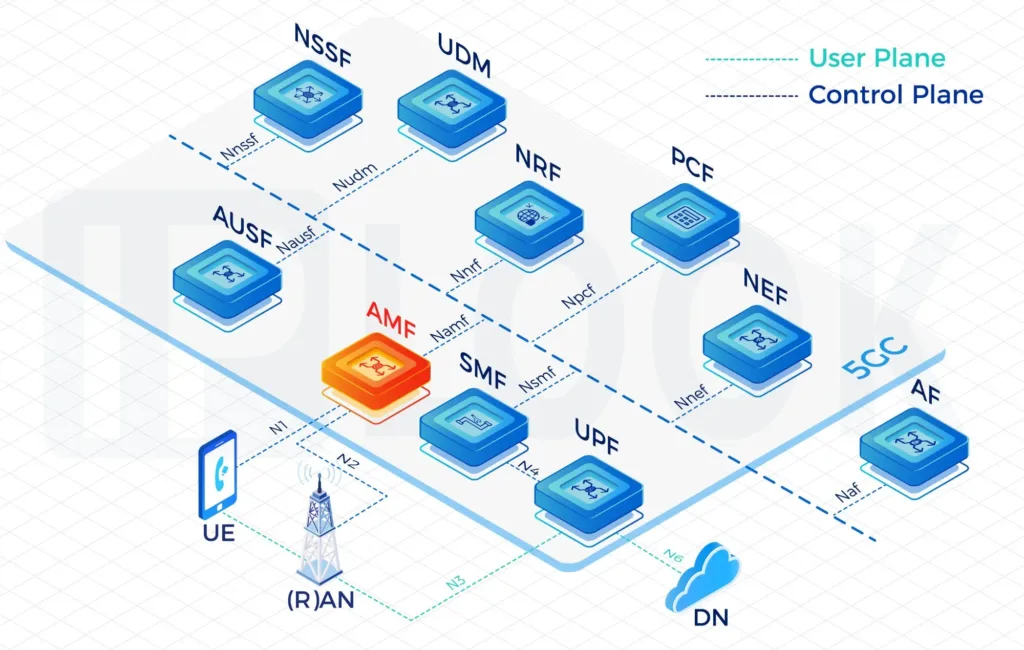
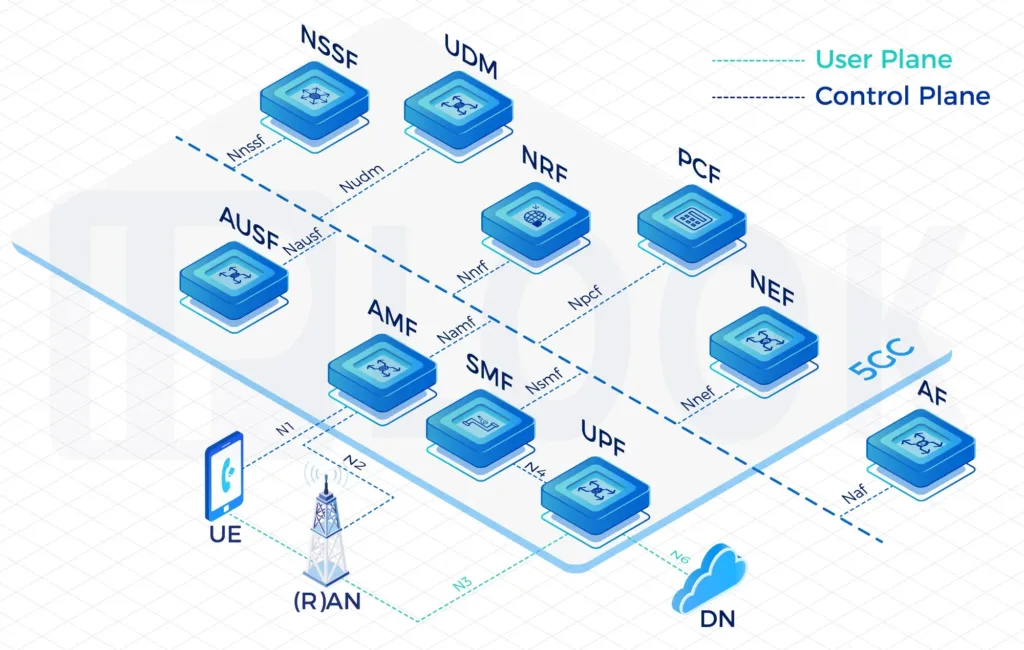
Our High-Performing Core Network
Fully virtualizable on VMware, K8S, Docker and OpenStack containers
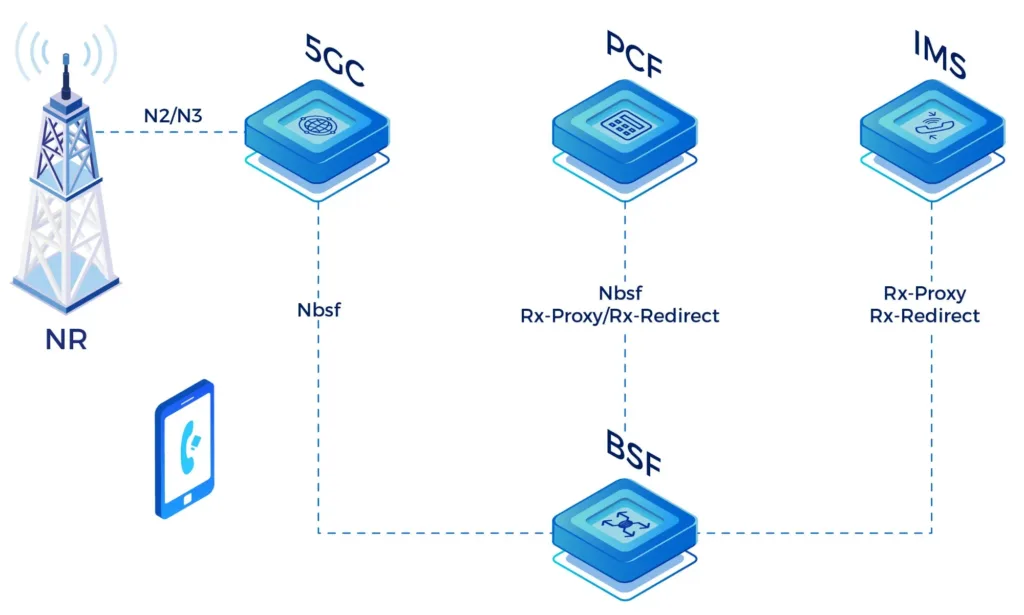
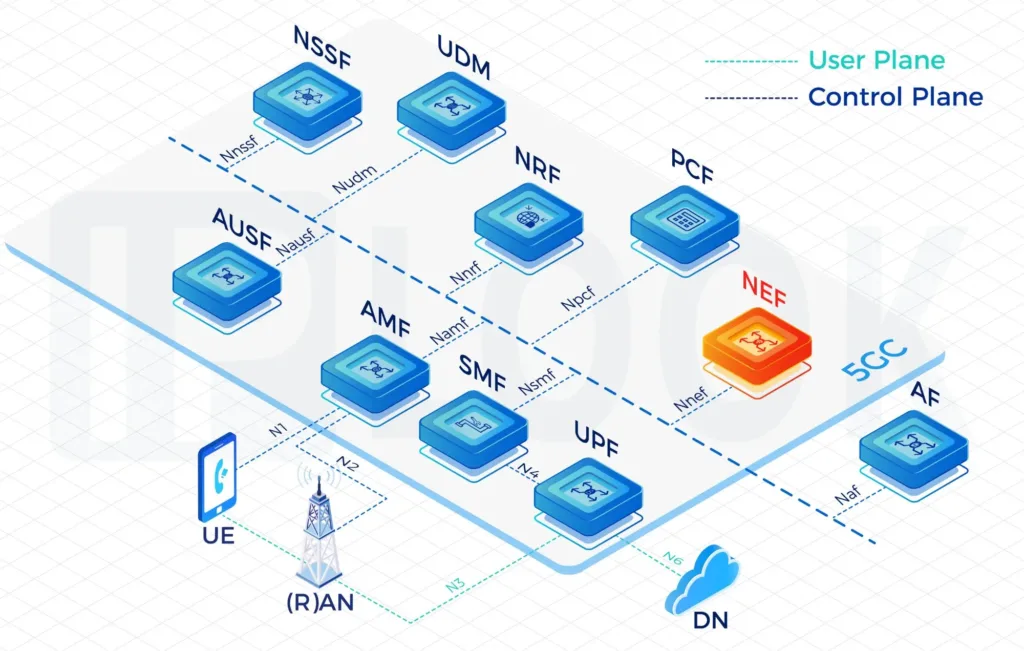
Binding Support Function(BSF)
The primary function of BSF is to act as a binding middleware between PDU sessions and AF, ensuring that in deployments with multiple individually addressable PCF/NEF/AF/MBSF/NWDAF/TSCTSF, session information for a specific PDU session can be queried through the BSF. This supports policy control and session management.
Key Benefits

Session Binding and Policy Mediation

Rx Redirection and Proxy Support

Dynamic Policy Coordination

Network Function Interaction

Security and Authorization Control
PDU Session Information Query
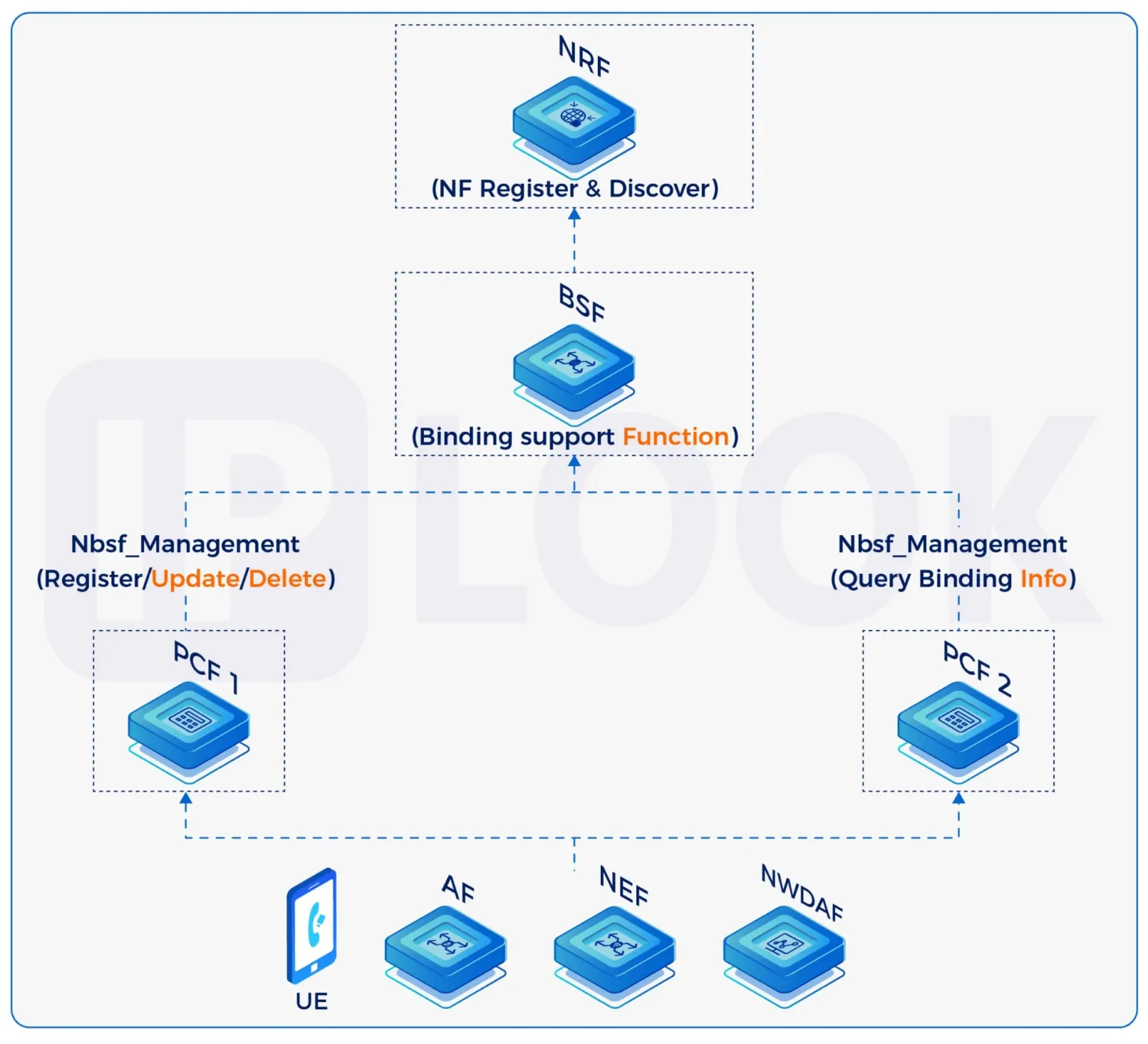
BSF Solution
- Supports multi-PCF policy binding and slice management.
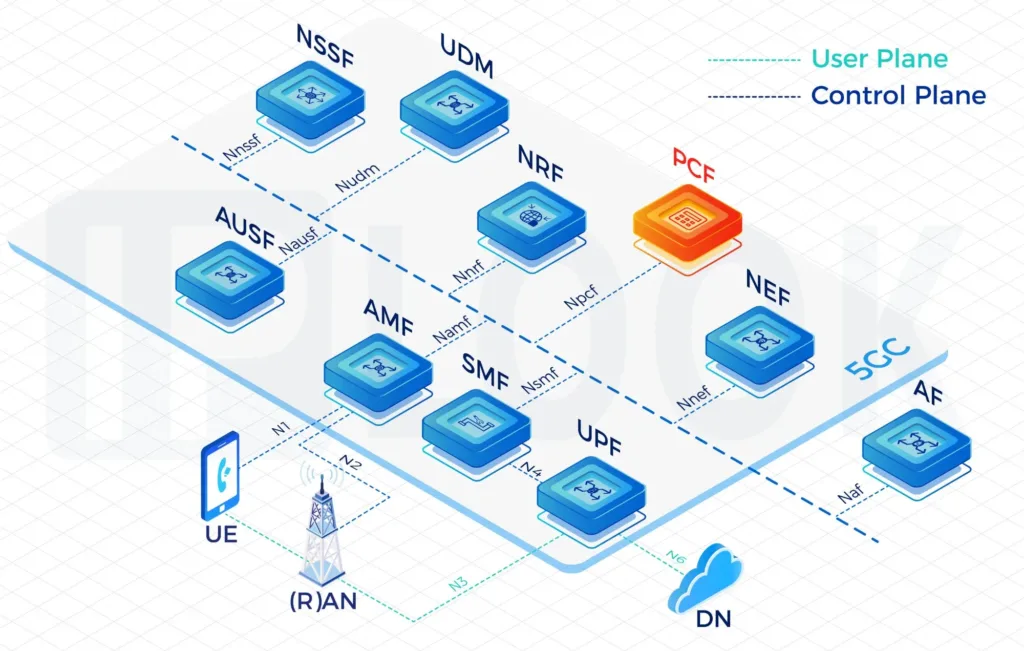
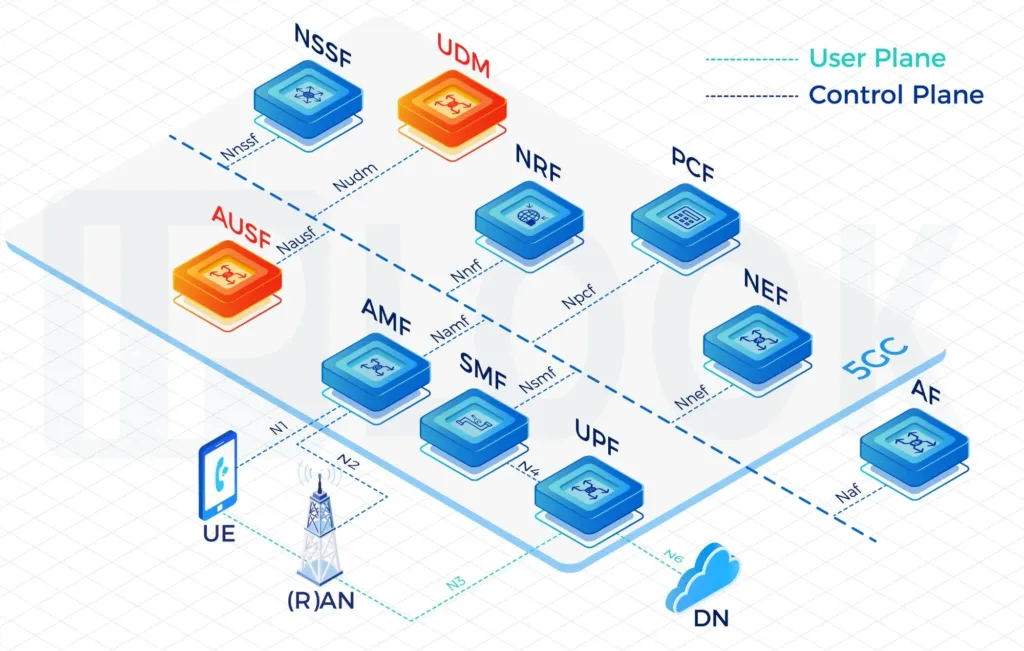
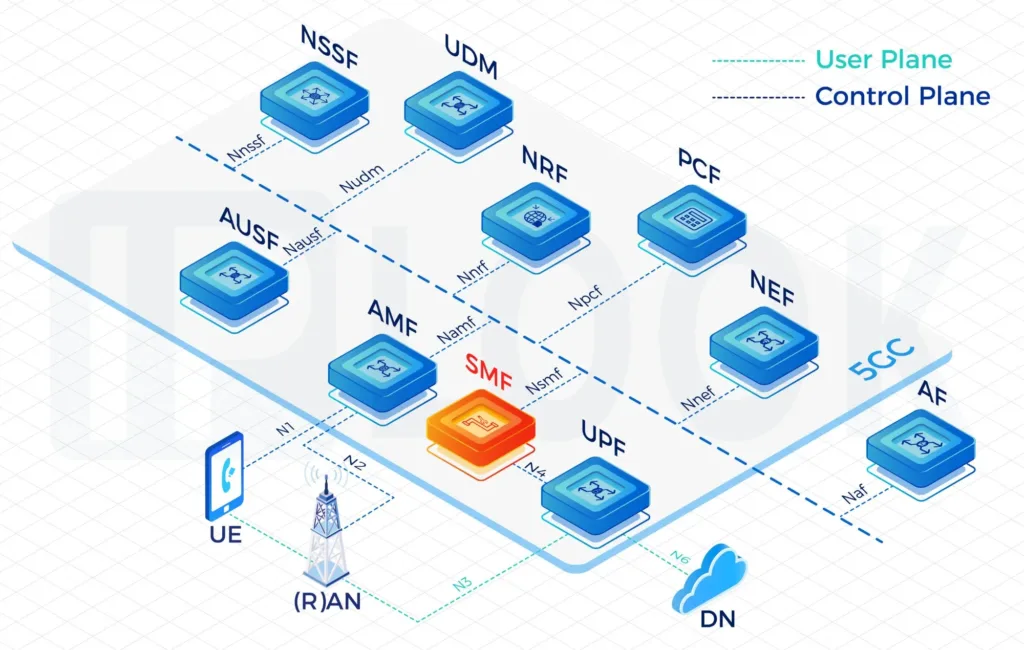
- During the deployment of 5G SA networks, with the increasing complexity of policy control, BSF has become a critical component to ensure policy consistency in multi-PCF environments. By centrally managing the binding relationships between UEs and PCFs, BSF ensures that policy requests are quickly and accurately routed to the appropriate PCF instance. BSF supports network slicing, roaming, and cross-domain policy control, and works in coordination with core network elements such as UDM and NEF to achieve flexible and scalable policy distribution capabilities. This architecture is a key part of the 5G core network policy control system, providing strong support for operators to reduce operational complexity and improve network policy management efficiency.
Features
Interfaces/Protocols
- NBSF
- Network Protocols: IPv4/IPv6
- Management and Maintenance Protocols: HTTP, HTTPS, SFTP, SSH
- Signaling Protocols: HTTP 2, Diameter
Reliability
- Distributed Deployment: Supports distributed deployment; service failure at a single point does not affect other nodes; service nodes support load balancing and dynamic scaling; service nodes support 1+1 hot standby or N+M cold standby; supports service migration upon node failure.
- Supports Active-Standby Disaster Recovery: When a single BSF node fails, the system automatically switches to the standby BSF to provide services, with a switchover time of no more than 10 seconds.
- Supports Active-Active Disaster Recovery: Supports multiple BSF nodes providing services through load balancing.
Security Features
- Supports security features such as DOS/DDOS attack protection and SQL injection prevention.
- Supports encrypted transmission of message data.
- Supports overload protection.
Deployment Methods
- Supports bare-metal server deployment.
- Supports KVM virtual machine deployment.
- Supports Kubernetes and OpenStack.
Network Management
- Signaling Tracing
- Topology Management
- Log Management
- Alarm Management
- System Resource Monitoring