As 5G private networks expand across industry verticals, choosing the right core network deployment model becomes a critical step. For small- to medium-scale use cases with limited users and constrained resources, centralized deployment offers a highly efficient and cost-effective solution.
In this first article of IPLOOK’s 5GC Deployment Series, we explore how centralized deployment enables rapid, reliable rollout of private 5G networks—ideal for pilot projects, labs, campuses, and compact industrial sites.
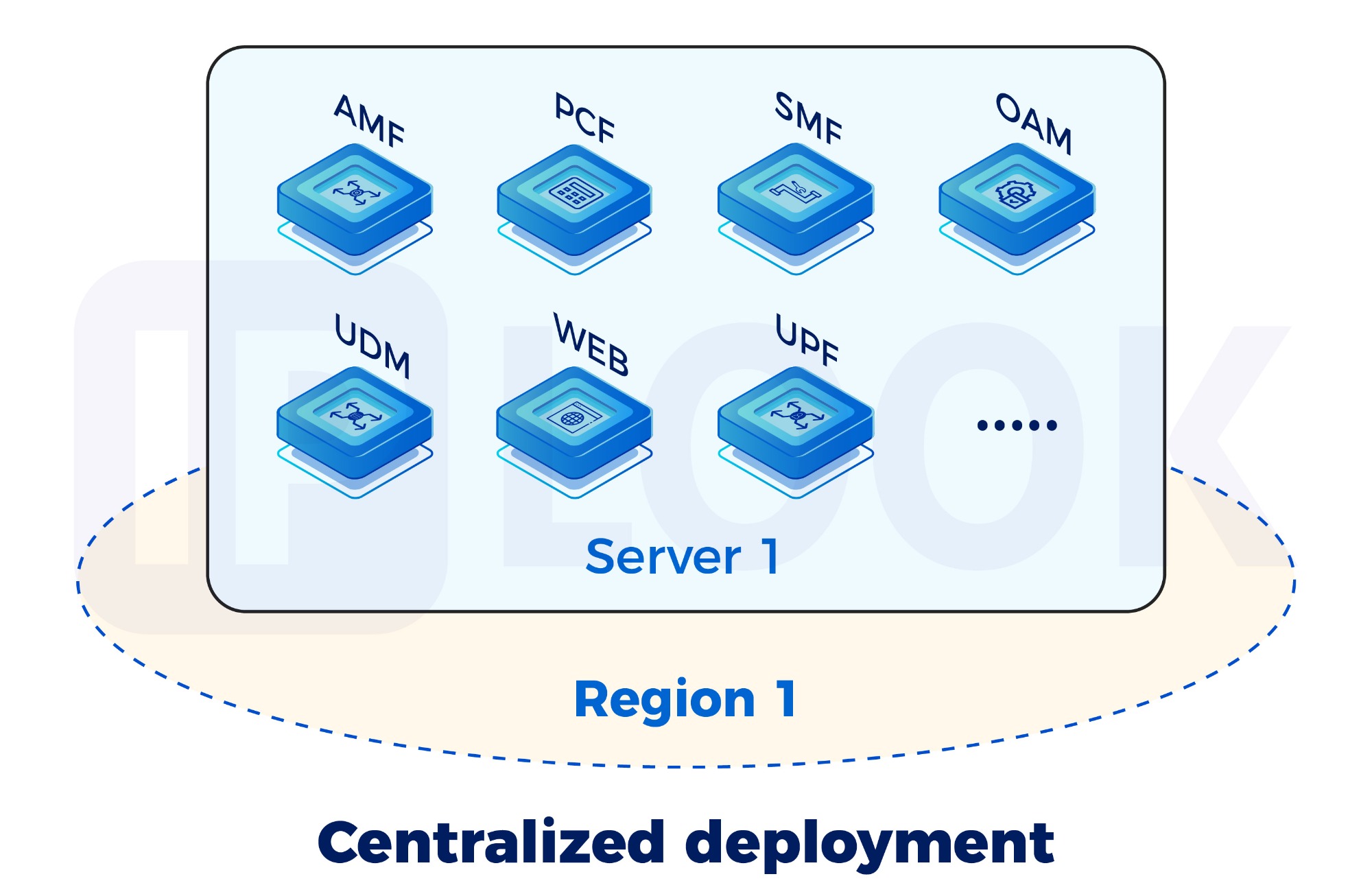
What is Centralized Deployment?
Centralized deployment consolidates all 5G Core Network functions—including AMF, SMF, UPF, UDM, AUSF—into a single x86 or ARM general-purpose server. Control plane and user plane components operate on the same physical infrastructure, enabling internal communication across interfaces with minimal latency and resource consumption.
It’s a one-box 5GC architecture optimized for light workloads, faster rollout, and streamlined management.
Key Advantages of IPLOOK’s Centralized 5GC
All-in-One Deployment
All 5GC network functions run on a single server—simplifying installation, integration, and operations. The system can be up and running in hours.
Cost-Efficient, Resource-Friendly
Minimal hardware footprint means lower capital and operating expenses. Ideal for budget-conscious projects or MVP deployments.
Internal Interfaces, Lower Latency
With all components running locally, signaling between functions (N1, N2, N4, N6, N8, etc.) happens internally, reducing bandwidth usage and boosting system responsiveness.
Full Voice & Messaging Support
Out-of-the-box support for:
-
VoNR (Voice over New Radio)
-
VoLTE (Voice over LTE)
-
EPS Fallback & CSFB
-
Messaging protocols like SMS, IMS, and USSD
Where It Works Best
Centralized 5GC deployment is purpose-built for environments that don’t require geographic redundancy or horizontal scaling, including:
-
Campus networks (universities, R&D zones)
-
Pilot projects & labs (government or industrial proofs of concept)
-
Compact private networks (factories, ports, warehouses, energy sites)
-
Enterprise testbeds (office campuses, smart buildings)
These use cases typically feature limited concurrent users, moderate bandwidth needs, and a preference for fast deployment with minimal infrastructure investment.