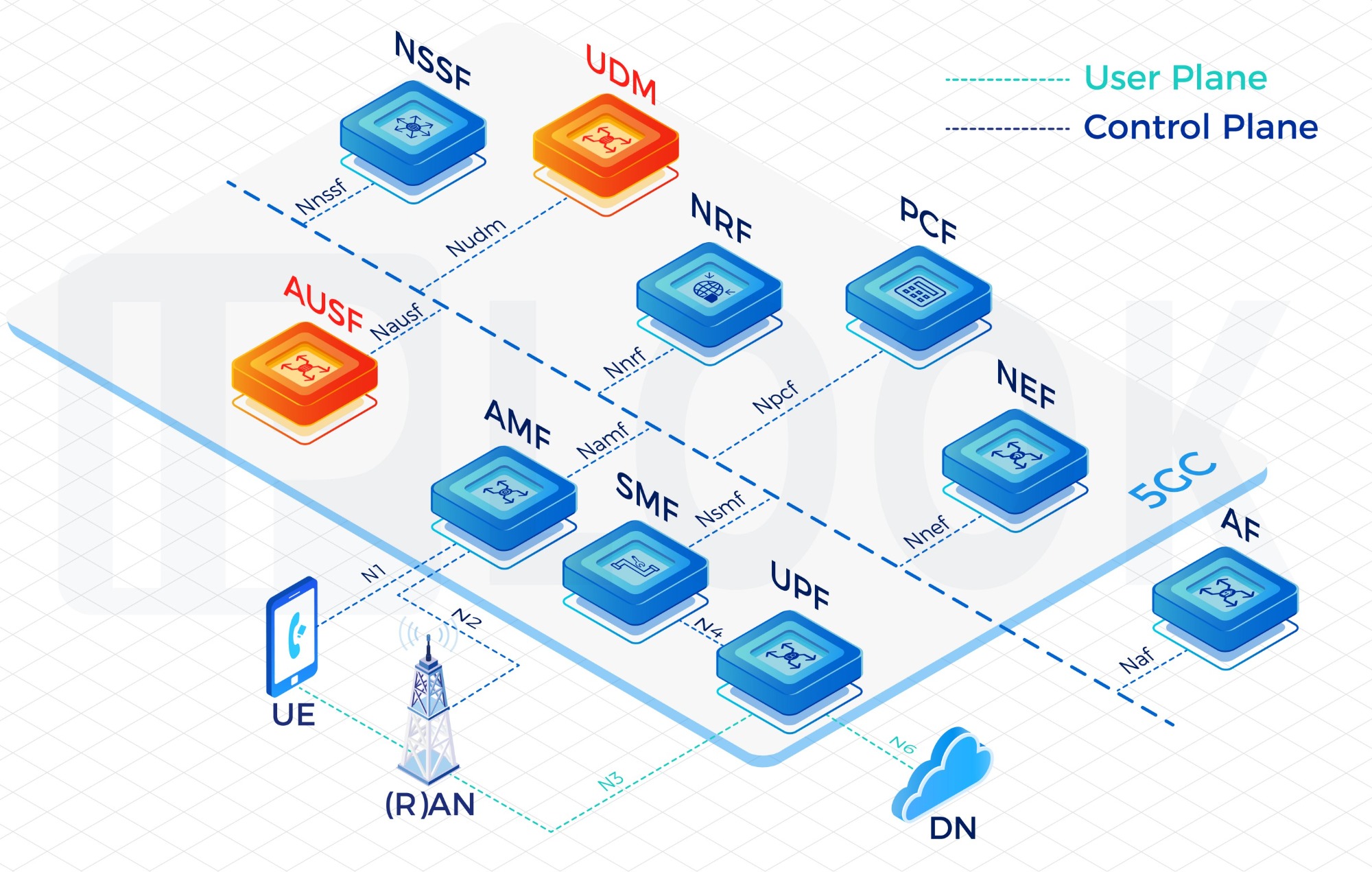
Imagine a 5G network without memory — it wouldn’t know who you are, what services you have, or what network slice you belong to. Every time you connect, it would be like meeting the network for the first time.
The Unified Data Management (UDM) function prevents that from happening. Acting as the intelligent database and identity manager of the 5G Core, UDM stores and manages all subscriber-related information. It ensures that every connection, authentication, and policy decision is based on trusted and consistent data.
The Core Responsibilities of UDM
UDM serves as the central repository for user subscription, authentication, and mobility information. It works closely with other network functions to ensure a seamless and secure user experience.
1. Subscription and Profile Management
UDM stores subscriber profiles, including user identifiers, service entitlements, and policy settings. Whenever a device connects, UDM provides the necessary data so the network knows what services and QoS levels to apply.
2. Authentication and Security
In cooperation with AUSF (Authentication Server Function), UDM authenticates users and devices to verify their identity before granting access. It securely handles credentials and ensures that only legitimate users can connect to the network.
3. Mobility and Session Continuity
UDM maintains essential information for session and mobility management, allowing users to move between cells or networks without losing connectivity. It ensures that service continuity is always preserved, even across different access types.
Inside the UDM Workflow
When a user device (UE) attempts to connect to the 5G Core, the AMF requests subscription and authentication data from UDM. UDM communicates with the AUSF to verify the user’s identity, retrieves the subscriber’s profile, and returns the information to the AMF.
Based on that data, the network applies the correct service policies, QoS configurations, and session parameters. Throughout the user’s connection, UDM remains the trusted source for user data consistency across all core network functions.
Why UDM Matters in 5G
UDM ensures that user information is unified, accurate, and accessible to authorized network functions. Without it, the 5G Core would lose the foundation for authentication, policy enforcement, and service personalization.
As operators deploy millions of subscribers and billions of IoT devices, UDM’s scalability and reliability become essential to maintaining performance and security. It enables unified user management across distributed networks and cloud-based cores.
UDM in Real-World Applications
Subscriber Management: Centralized storage of subscriber data for mobile operators, MVNOs, and enterprise networks.
IoT Authentication: Validates device identities for massive IoT deployments across industries.
Policy Enforcement: Works with PCF to ensure each user receives services according to their profile.
Seamless Roaming: Supports consistent authentication and service continuity across local and visited networks.
Edge and Cloud Integration: Provides synchronized user data for distributed, cloud-native 5G deployments.
UDM: The Memory of the 5G Core
UDM is the brain that remembers — who the user is, what they’re allowed to do, and how they connect. It ensures that every interaction between device and network is secure, personalized, and uninterrupted.
As 5G evolves toward 6G, UDM will continue to be the foundation of digital identity, enabling a smarter, more connected, and trusted communication ecosystem.