Space-air-ground integrated networks (SAGINs) are envsioned to provide seamless network services to spatial, aerial, maritime and gound users, satisfying the future network requirements on all-time, all-domain, and all-space communications and interconnected networking.
From the perspective of market and business development, both general users and industry users have shown an increasingly strong demand for seamless integration of satellite and ground communication. General users have evolving needs for personal mobile communication, expecting seamless coverage and ubiquitous access anytime, anywhere. Industry users, on the other hand, require ubiquitous connectivity provided by satellite and ground networks for emergency communication, transportation, marine coverage, and pervasive low-altitude scenarios.
The architecture of the integrated satellite and ground network can be mainly divided into Satellite Relay Mode and Terminal-satellite Direct Connection Mode. The latter includes traditional terminal direct connection based on private protocols, 3GPP NTN terminal-satellite direct connection, and connection of unmodified commercial terminals, enabling coverage in different scenarios and network complementarity.
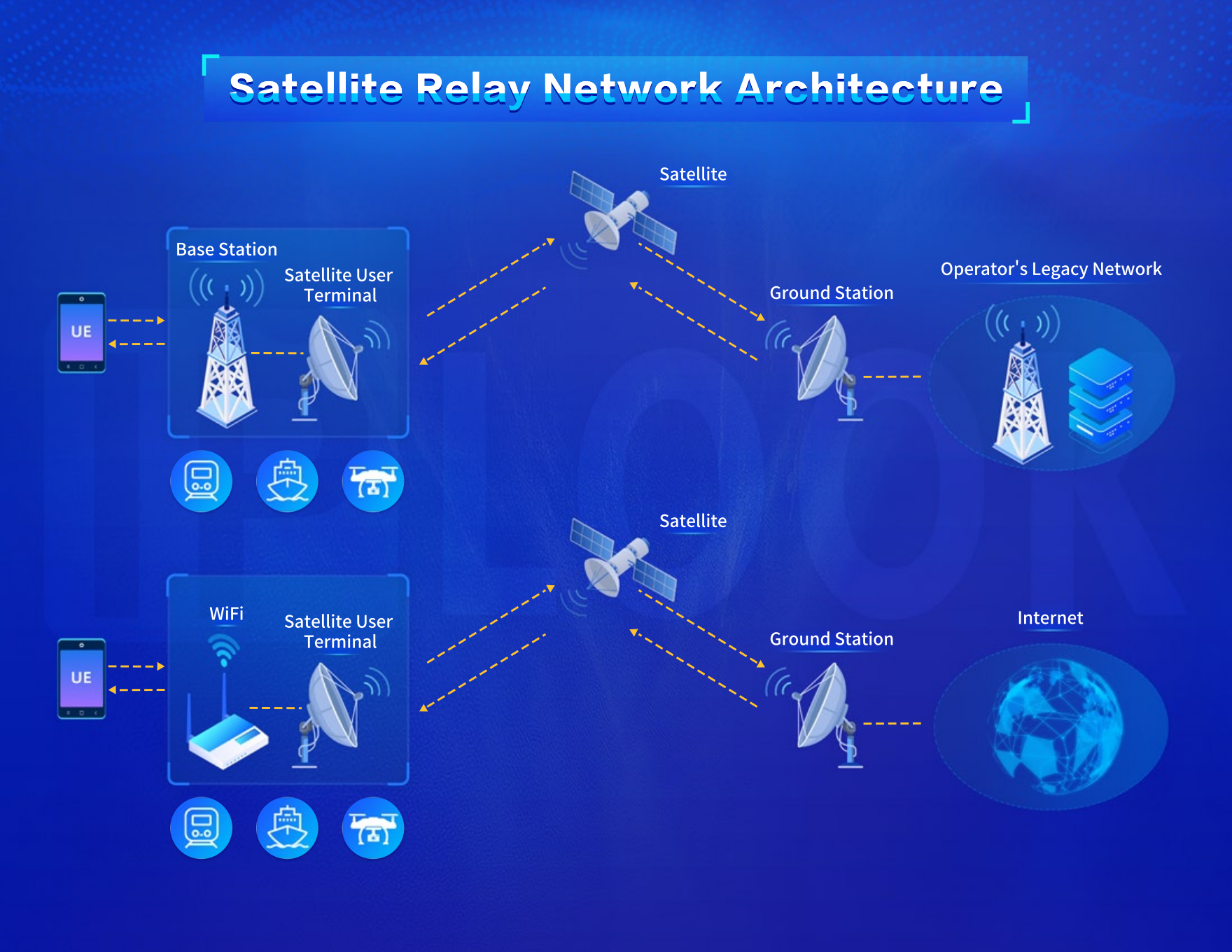
Satellite Relay Mode
Satellite Relay Mode involves user terminals, specific scenario devices, space-based networks, land-based networks, and user access to ground stations/Wi-Fi. Users connect to satellites through dedicated satellite user stations, and the satellites serve as link transmitters. This mode is suitable for scenarios with concentrated users and clear mobility routes, replacing wired fiber backhaul. It is currently widely used in special scenario coverage and emergency communication in various industries.
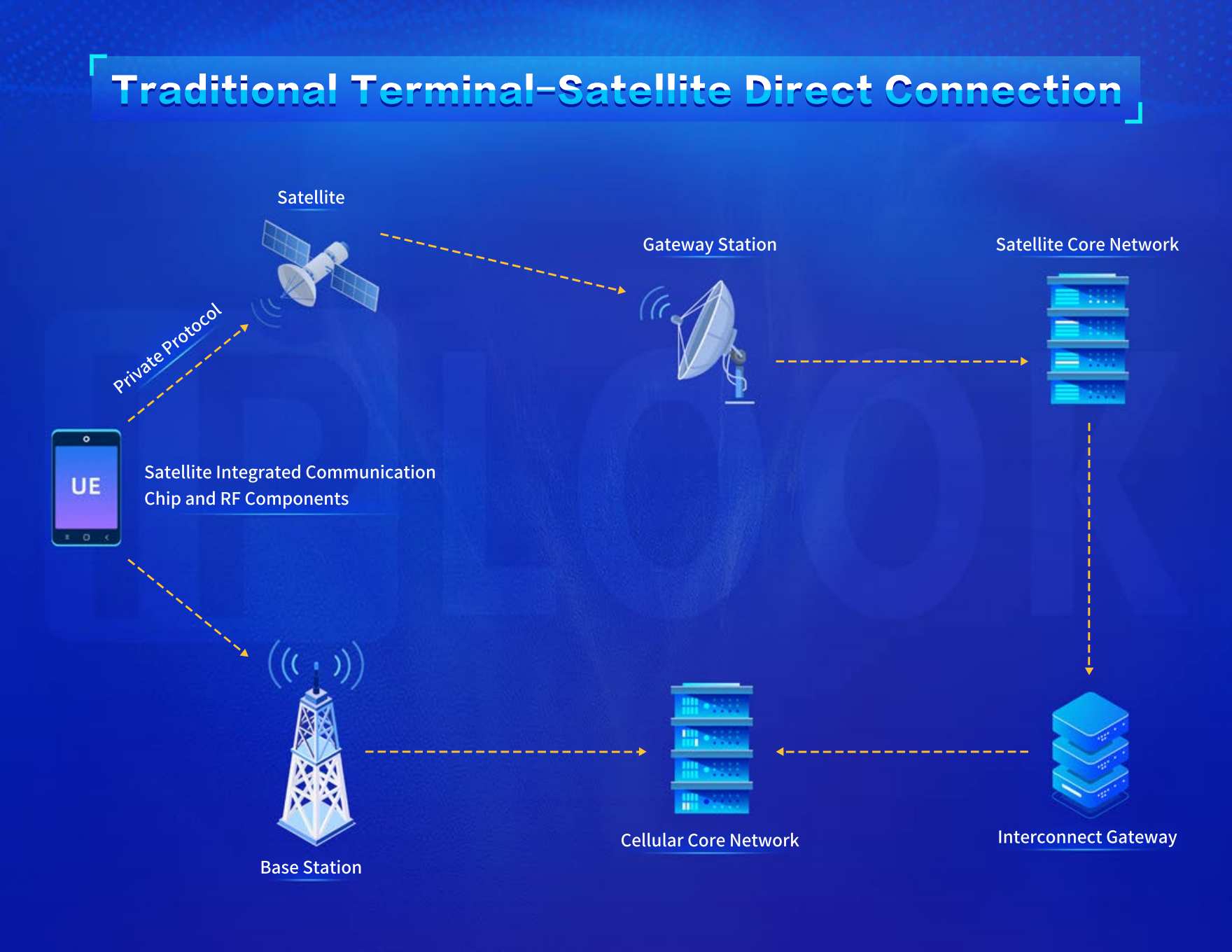
Traditional Terminal-Satellite Direct Connection Mode
In this mode, cellular phones are equipped with satellite communication chips to connect to satellites, while satellites are connected to the cellular core network through gateways, enabling intercommunication. Satellites and cellular networks operate with independent architectures, systems, and frequencies.
This traditional mode mainly collaborates with in-orbit satellites, without the need for frequency licenses. Cellular base stations and core networks remain unchanged, and terminals can achieve interconnection through multi-mode upgrades and deployment of gateway devices. This mode has the advantage of fast deployment and can quickly address the needs of cellular dead zones for emergency communication and small data collection in remote areas. However, due to the current limitations of in-orbit satellites, it can only support messaging, voice, and narrowband services, making it difficult to meet the requirements of broadband services. The industry is also limited by closed communication systems, resulting in small-scale deployments and high costs.
3GPP NTN Terminal-Satellite Direct Connection Mode
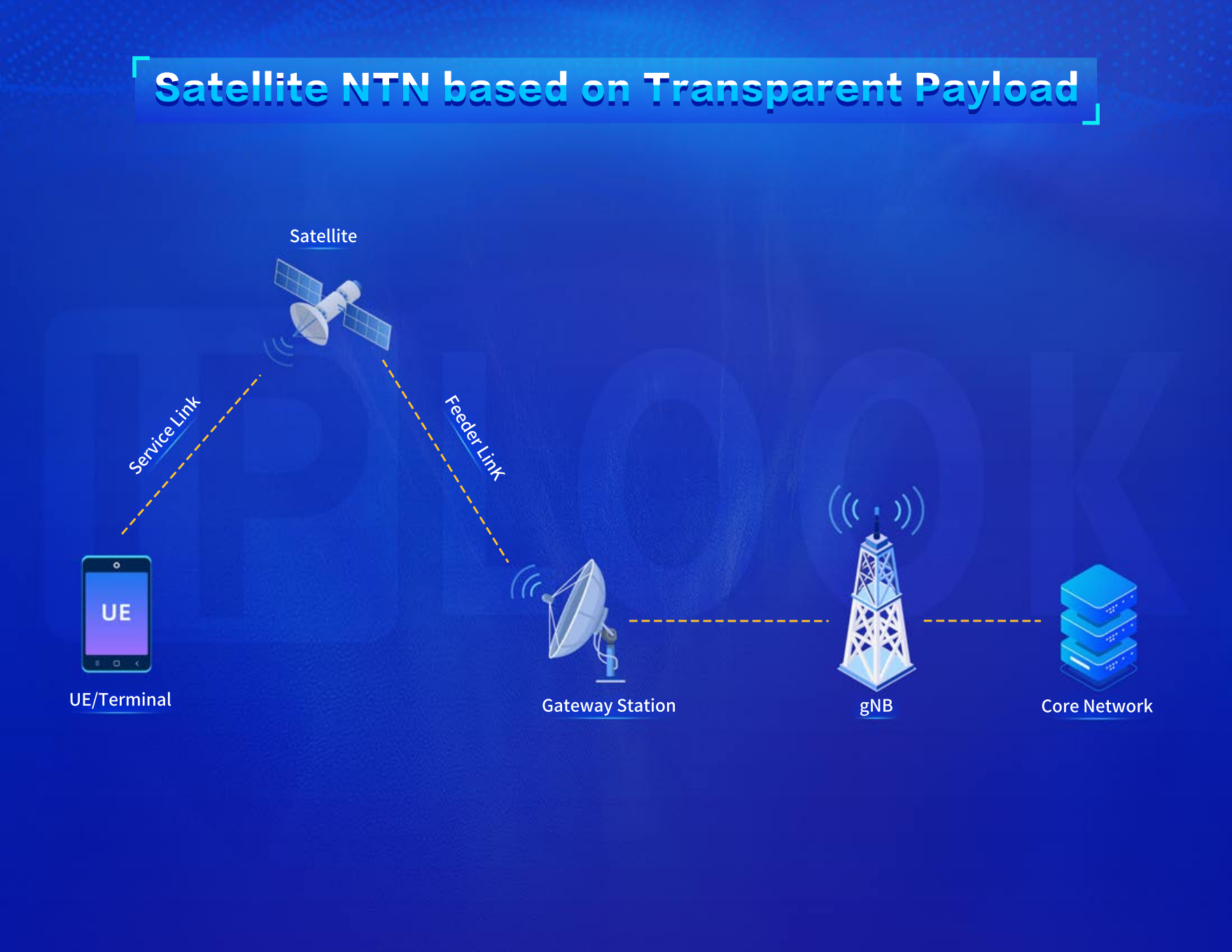
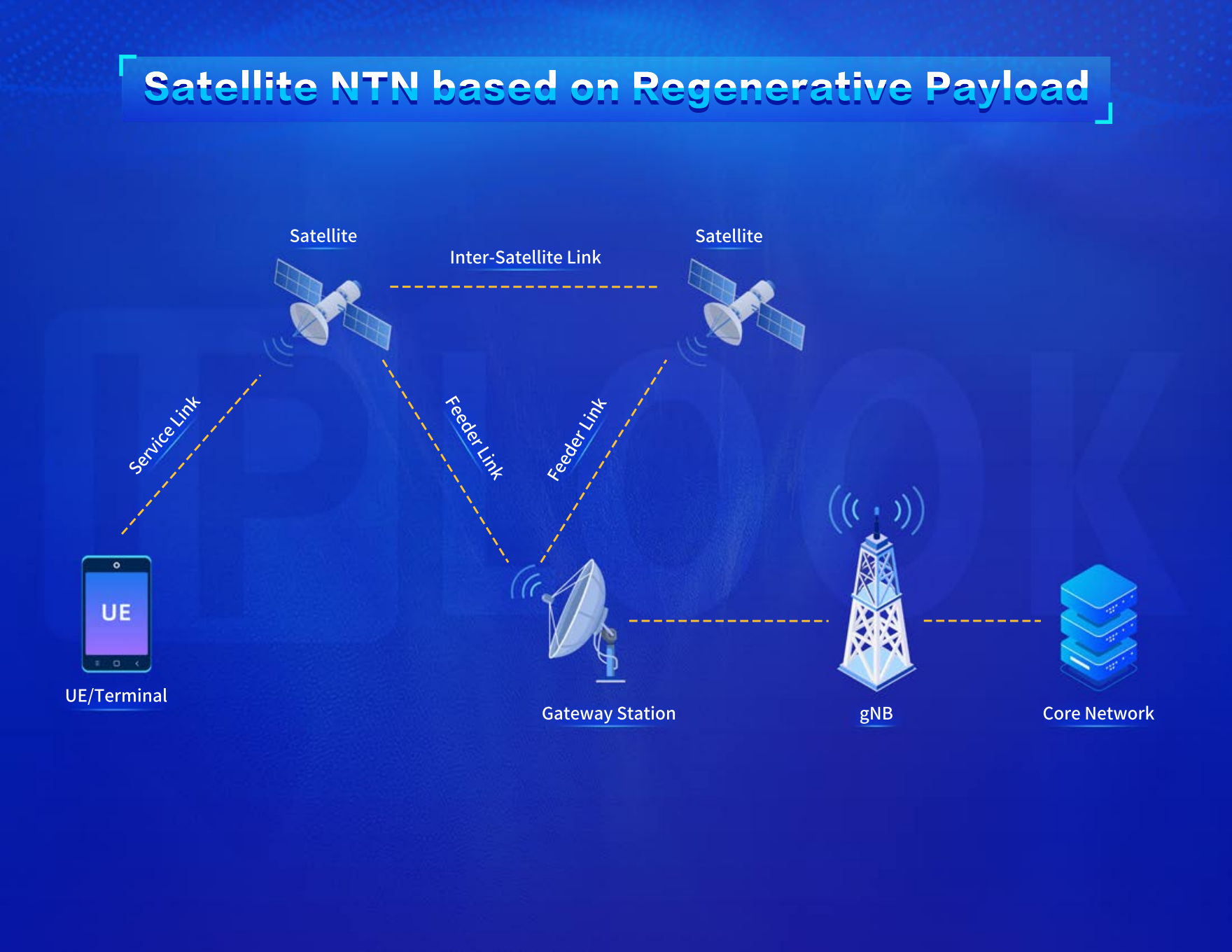
The 3GPP NTN Terminal-Satellite Direct Connection Mode is an important networking model for future integrated satellite and ground communication. It includes two network architectures: Satellite NTN based on Transparent Payload and Satellite NTN based on Regenerative Payload Architecture.
· Satellite NTN based on Transparent Payload Architecture: Transparent Payload acts as a relay node on the network side. It changes the frequency carrier of the uplink RF signal, filters and amplifies it before transmitting it on the downlink, while the signal waveform remains unchanged. The gateway station only transmits the signal, and different transparent satellites can connect to the same ground base station.
· Satellite NTN based on Regenerative Payload Architecture: In this architecture, regenerative forwarding payload acts as an effective payload that converts and amplifies the uplink RF signal before transmitting it on the downlink. It functions similarly to having partial base station and core network capabilities on the satellite, including DU uplink, base station uplink, UPF uplink, simplified core network uplink, and other modes. Additionally, the satellite payload can provide inter-satellite links, allowing User Equipment (UE) to access the core network through inter-satellite links, and gNBs on different satellites may connect to the same ground-based core network.
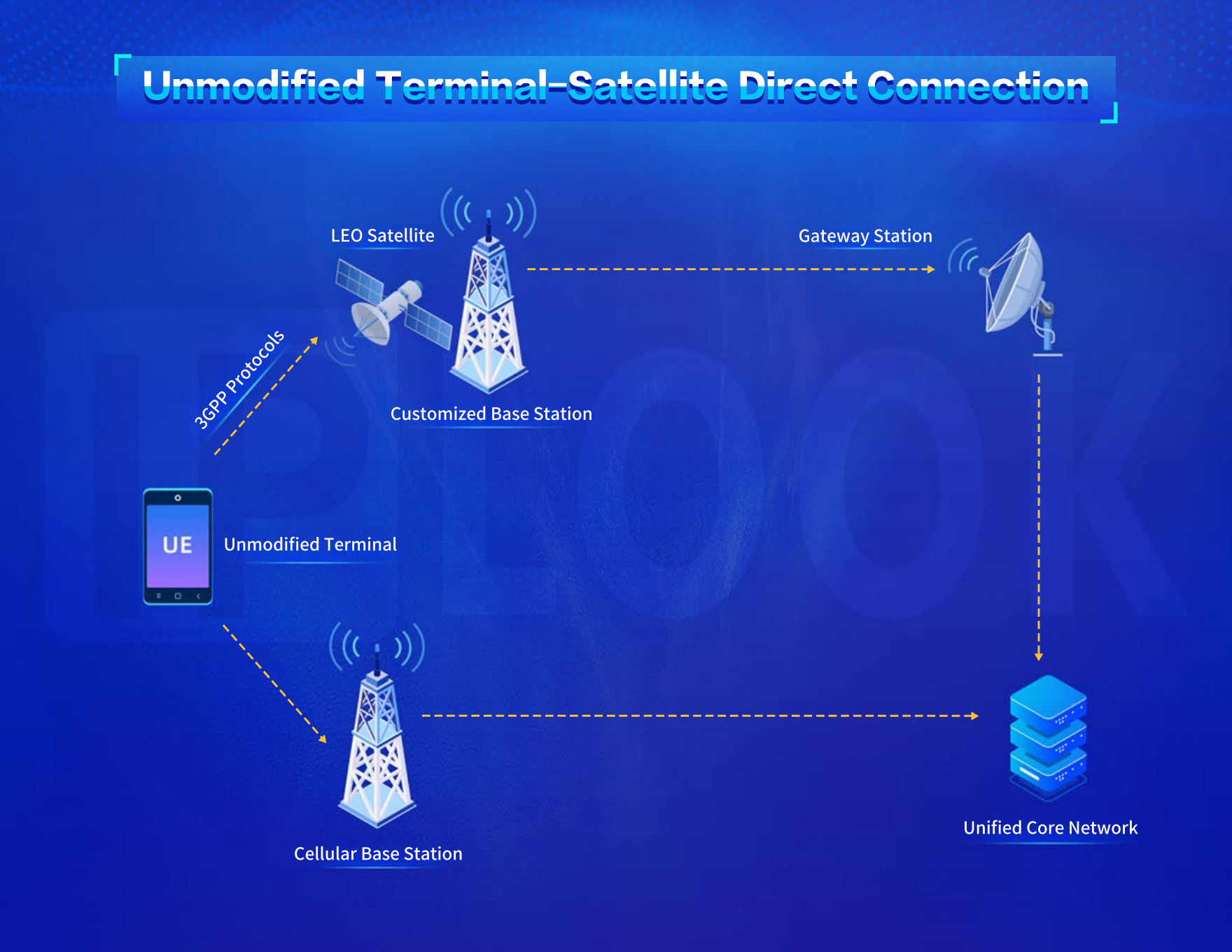
The Unmodified Terminal-Satellite Direct Connection
The Unmodified Terminal-Satellite Direct Connection Architecture does not change the mobile phone terminal, and the satellite and base station are customized to adapt to the cellular terminal and air interface protocol, so that the unmodified smartphones can be connected to the satellite network. This architecture cannot utilize the on-orbit constellation and requires the use of terrestrial cellular frequencies to solve frequency licensing and license issues. It also requires customized constellation design and satellite base station design, which is difficult and costly to implement, but it is suitable for the early stage of network construction. When the penetration rate of NTN services is low, satellite services can be quickly promoted.
In the future, the SAGIN is an important goal for future network development and an inevitable trend for the integrated development of mobile communications and satellite communications.