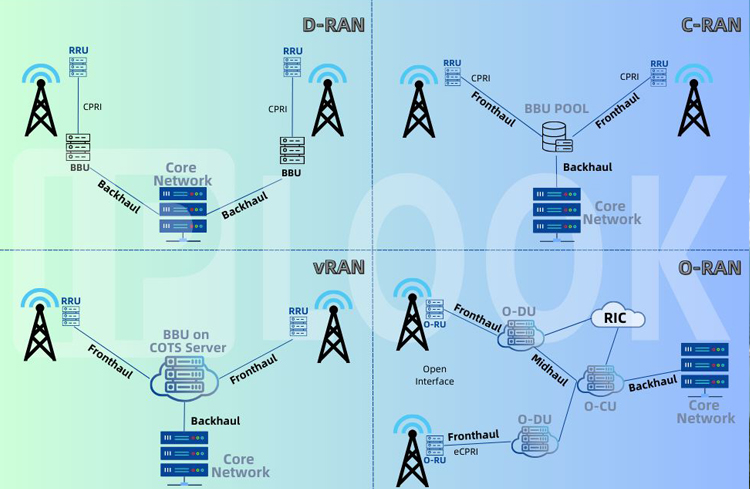
The architecture of Radio Access Network (RAN) has undergone significant transformations over the years to meet evolving requirements and optimize costs. Four major architectural approaches have emerged: D-RAN, C-RAN, vRAN, and O-RAN. Each approach brings unique benefits to the telecommunications industry.
D-RAN
D-RAN, or Distributed RAN, is an early architecture where the Remote Radio Unit (RRU) and Baseband Unit (BBU) are co-located at each cell site. This approach distributes the radio functions across multiple sites, with backhaul connections linking them to the core network. D-RAN provides localized processing and reduces the load on backhaul links, but it can be costlier due to the need for equipment at each cell site.
C-RAN
C-RAN, or Centralized RAN, introduces a centralized architecture by moving the baseband processing to a central location known as the BBU pool. In C-RAN, RRUs are deployed at the cell sites and connected to the BBU pool through high-capacity fiber links. This consolidation of processing resources enables better resource utilization and cost savings, as BBUs can be shared among multiple cell sites.
vRAN
vRAN, or Virtual RAN, also referred to as Cloud RAN, leverages Network Function Virtualization (NFV) principles to virtualize proprietary RAN systems onto Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) hardware. By virtualizing RAN functions as software, vRAN reduces reliance on dedicated hardware, enabling operators to scale their networks more efficiently and introduce new services faster. This virtualization also brings flexibility and agility to RAN deployments.
O-RAN
The latest addition to the RAN architecture landscape is O-RAN, or Open RAN. O-RAN extends the principles of openness and standardization to RAN design. In this architecture, the RRH (Remote Radio Head) and BBU (or virtual BBU) combination is split into three components: the Centralized Unit (CU), Distributed Unit (DU), and Radio Unit (RU). O-RAN emphasizes open interfaces and standards, allowing multiple vendors to provide components that can seamlessly integrate with one another. This open approach fosters vendor competition and innovation while preventing vendor lock-in.
The evolution of RAN architecture has been driven by the need for greater flexibility, efficiency, and cost optimization in mobile networks. Each approach—D-RAN, C-RAN, vRAN, and O-RAN—offers distinct advantages and addresses specific challenges faced by MNO. As the telecommunications industry continues to evolve, it is likely that future RAN architectures will build upon these foundations to meet the demands of emerging technologies and customer expectations.