Nowadays, networking has become a crucial part of our daily lives. To implement network services for users, base station plays an essential role to constitute a complete network system by transmitting signals.
What is base station? This article will take 4G LTE base station (eNodeB) for example to elaborate.
Base station consists of four major parts:
1. Antenna System
Generally, a base station contains several antennas mounted on its top, mainly responsible for the transmission and reception of signals, connected to the RRU.
2. RRU( Remote Radio Unit)
RRU can be divided into several sectors for the transmission of 2G, 3G, 4G and even 5G signals. The signal generation and extraction of radio signals are performed here.
3. BBU(Baseband Unit)
Placed in the equipment room and connected with RRU via optical fiber, BBU, the core of the base station, is a unit that processes the original signal.
4. Physical support
It mainly includes electrical power system, backup battery (to prevent power failure), transmission equipment, and air conditioning system (to maintain the optimal temperature for regular operation).
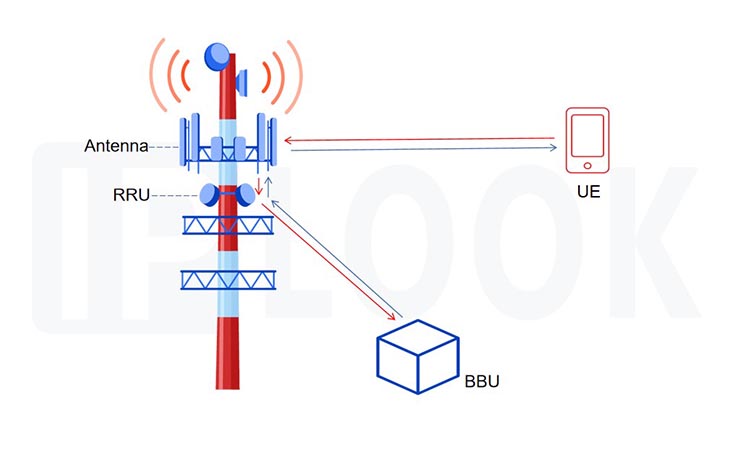
Based on the above components, they work in collaboration to form a base station that transmits signals. With multiple base stations composing a tightly connected network, seamless coverage of network services are provided to users.
The evolution in the 5G era
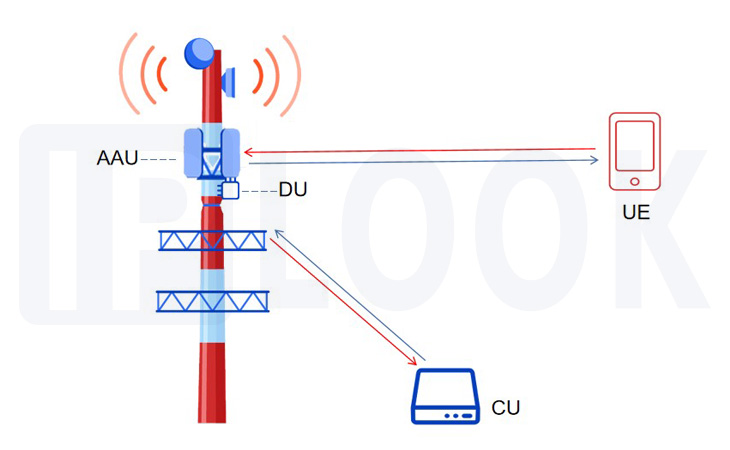
In 5G networks, 4G RRUs and antennas are merged into Active Antenna Units (AAUs). BBUs are divided into Centralized Units (CUs) and Distributed Units (DUs). The DUs are deployed at the AAU. This architecture can simplify site deployment to reduce transmission consumption and improve overall performance.
Contact us for more information!